Triptolide Inhibits the Proliferation of Immortalized HT22 Hippocampal Cells Via Persistent Activation of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase-1/2 by Down-Regulating Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase-1 Expression
- PMID: 19893732
- PMCID: PMC2773400
- DOI: 10.3340/jkns.2009.46.4.389
Triptolide Inhibits the Proliferation of Immortalized HT22 Hippocampal Cells Via Persistent Activation of Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase-1/2 by Down-Regulating Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase-1 Expression
Abstract
Objective: Triptolide (TP) has been reported to suppress the expression of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatase-1 (MKP-1), of which main function is to inactivate the extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2 (ERK-1/2), the p38 MAPK and the c-Jun N-terminal kinase-1/2 (JNK-1/2), and to exert antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic activities. However, the mechanisms underlying antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic activities of TP are not fully understood. The purpose of this study was to examine whether the down-regulation of MKP-1 expression by TP would account for antiproliferative activity of TP in immortalized HT22 hippocampal cells.
Methods: MKP-1 expression and MAPK phosphorylation were analyzed by Western blot. Cell proliferation was assessed by (3)H-thymidine incorporation. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) against MKP-1, vanadate (a phosphatase inhibitor), U0126 (a specific inhibitor for ERK-1/2), SB203580 (a specific inhibitor for p38 MAPK), and SP600125 (a specific inhibitor for JNK-1/2) were employed to evaluate a possible mechanism of antiproliferative action of TP.
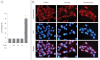
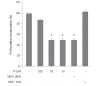
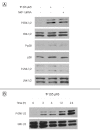
Results: At its non-cytotoxic dose, TP suppressed MKP-1 expression, reduced cell growth, and induced persistent ERK-1/2 activation. Similar growth inhibition and ERK-1/2 activation were observed when MKP-1 expression was blocked by MKP-1 siRNA and its activity was inhibited by vanadate. The antiproliferative effects of TP, MKP-1 siRNA, and vanadate were significantly abolished by U0126, but not by SB203580 or SP600125.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that TP inhibits the growth of immortalized HT22 hippocampal cells via persistent ERK-1/2 activation by suppressing MKP-1 expression. Additionally, this study provides evidence supporting that MKP-1 may play an important role in regulation of neuronal cell growth.
Keywords: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase-1/2; HT22 hippocampal cell; Mitogen-activated protein kinase; Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1; Proliferation; Triptolide.
Figures


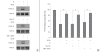
Similar articles
-
Conditional expression of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatase MKP-1 preferentially inhibits p38 MAPK and stress-activated protein kinase in U937 cells.J Biol Chem. 1997 Jul 4;272(27):16917-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.27.16917. J Biol Chem. 1997. PMID: 9202001
-
Compartment-specific regulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) by ERK-dependent and non-ERK-dependent inductions of MAPK phosphatase (MKP)-3 and MKP-1 in differentiating P19 cells.Biochem J. 2000 Dec 15;352 Pt 3(Pt 3):701-8. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 11104676 Free PMC article.
-
Cyclic strain stress-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatase 1 expression in vascular smooth muscle cells is regulated by Ras/Rac-MAPK pathways.J Biol Chem. 1999 Sep 3;274(36):25273-80. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.36.25273. J Biol Chem. 1999. PMID: 10464250
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phosphatase-3 (MKP-3) displays a p-JNK-MAPK substrate preference in astrocytes in vitro.Neurosci Lett. 2014 Jul 11;575:13-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.05.039. Epub 2014 May 23. Neurosci Lett. 2014. PMID: 24861519 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Phosphatase (MKP)-1 in Nervous System Development and Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2015;51(3):1158-67. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-8786-6. Epub 2014 Jun 24. Mol Neurobiol. 2015. PMID: 24957007 Review.
Cited by
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 modulates regional effects of injurious mechanical ventilation in rodent lungs.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012 Jul 1;186(1):72-81. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201109-1593OC. Epub 2012 May 10. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22582160 Free PMC article.
-
Triptolide inhibits TGF-β1 induced proliferation and migration of rat airway smooth muscle cells by suppressing NF-κB but not ERK1/2.Immunology. 2014 Sep 29;144(3):486-94. doi: 10.1111/imm.12396. Online ahead of print. Immunology. 2014. PMID: 25267491 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of cancer cell death induction by triptolide: A comprehensive overview.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 10;10(2):e24335. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24335. eCollection 2024 Jan 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38293343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DUSP1 induces apatinib resistance by activating the MAPK pathway in gastric cancer.Oncol Rep. 2018 Sep;40(3):1203-1222. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6520. Epub 2018 Jun 25. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 29956792 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boutros T, Chevet E, Metrakos P. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/MAP kinase phosphatase regulation : roles in cell growth, death, and cancer. Pharmacol Rev. 2008;60:261–310. - PubMed
-
- Cerignoli F, Rahmouni S, Ronai Z, Mustelin T. Regulation of MAP kinases by the VHR dual-specific phosphatase : implications for cell growth and differentiation. Cell Cycle. 2006;5:2210–2215. - PubMed
-
- Chen LW, Wang YQ, Wei LC, Shi M, Chan YS. Chinese herbs and herbal extracts for neuroprotection of dopaminergic neurons and potential therapeutic treatment of Parkinson's disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2007;6:273–281. - PubMed
-
- Chen P, Li J, Barnes J, Kokkonen GC, Lee JC, Liu Y. Restraint of proinflammatory cytokine biosynthesis by mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. J Immunol. 2002;169:6408–6416. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

