Age-associated changes in the expression and deposition of vocal fold collagen and hyaluronan
- PMID: 19894402
- PMCID: PMC2782757
- DOI: 10.1177/000348940911801009
Age-associated changes in the expression and deposition of vocal fold collagen and hyaluronan
Abstract
Objectives: We investigated age-associated changes in the expression and deposition of collagen and hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid; HA) in aged vocal folds.
Methods: Thirty Sprague-Dawley rats were involved in this study. For gene expression analyses, 15 animals were divided into 3 age groups of young (2 month), adult (9 month), and elderly (18 month) rats. Real-time polymerase chain reaction testing was used to quantify the messenger RNA expression of procollagen types I and III, matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9, and HA synthases 1, 2, and 3. The remaining 15 animals were divided into 3 similar age groups and underwent histologic analyses designed to investigate age-associated changes in the deposition of collagen and HA.
Results: The results revealed down-regulated expression of procollagen types I and III, matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9, and HA synthases 1, 2, and 3 in adult and elderly vocal folds, compared to young vocal folds. Histologically, staining of collagen was dense in the vocal folds of adult and elderly rats, and HA was less dense in the vocal folds of adult and elderly rats than in young rats.
Conclusions: A slowdown in the expression of procollagens and matrix metalloproteinases was associated with dense collagen in aged vocal folds, as observed in elderly humans. A similar decrease in the expression of genes that code for HA synthase was consistent with a low density of extracellular matrix HA in the vocal folds of elderly rats.
Figures
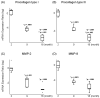
 . Median observations denoted by thick black line in each box. p values indicate a significant difference from (*) young and (**) adult vocal folds.
. Median observations denoted by thick black line in each box. p values indicate a significant difference from (*) young and (**) adult vocal folds.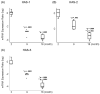
 . Median observations denoted by thick black line in each box. p values indicate a significant difference from (*) young and (**) adult vocal folds.
. Median observations denoted by thick black line in each box. p values indicate a significant difference from (*) young and (**) adult vocal folds.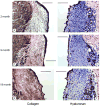
References
-
- Roy N, Stemple J, Merrill RM, Thomas L. Epidemiology of voice disorders in the elderly: preliminary findings. Laryngoscope. 2007;117:628–33. - PubMed
-
- Hirano M, Kakita Y. Cover-body theory of vocal fold vibration. In: Daniloff RG, editor. Speech science. San Diego, Calif: College Hill Press; 1985. pp. 1–46.
-
- Hammond TH, Gray SD, Butler JE. Age- and gender-related collagen distribution in human vocal folds. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2000;109:913–20. - PubMed
-
- Sato K, Hirano M, Nakashima T. Age-related changes of collagenous fibers in the human vocal fold mucosa. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2002;111:15–20. - PubMed
-
- Sato K, Hirano M. Age-related changes of elastic fibers in the superficial layer of the lamina propria of vocal folds. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1997;106:44–48. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

