Nicotine-mediated signals modulate cell death and survival of T lymphocytes
- PMID: 19896492
- PMCID: PMC2813922
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2009.10.020
Nicotine-mediated signals modulate cell death and survival of T lymphocytes
Abstract
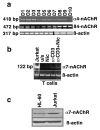
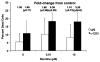
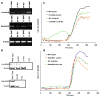
The capacity of nicotine to affect the behavior of non-neuronal cells through neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) has been the subject of considerable recent attention. Previously, we showed that exposure to nicotine activates the nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) transcription factor in lymphocytes and endothelial cells, leading to alterations in cellular growth and vascular endothelial growth factor production. Here, we extend these studies to document effects of nicotine on lymphocyte survival. The data show that nicotine induces paradoxical effects that might alternatively enforce survival or trigger apoptosis, suggesting that depending on timing and context, nicotine might act both as a survival factor or as an inducer of apoptosis in normal or transformed lymphocytes, and possibly other non-neuronal cells. In addition, our results show that, while having overlapping functions, low and high affinity nAChRs also transmit signals that promote distinct outcomes in lymphocytes. The sum of our data suggests that selective modulation of nAChRs might be useful to regulate lymphocyte activation and survival in health and disease.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





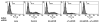
References
-
- Abraham RT, Weiss A. Jurkat T cells and development of the T-cell receptor signalling paradigm. Nat Rev Immunol. 2004;4:301–308. - PubMed
-
- Amos CI, Wu X, Broderick P, Gorlov IP, Gu J, Eisen T, Dong Q, Zhang Q, Gu X, Vijayakrishnan J, Sullivan K, Matakidou A, Wang Y, Mills G, Doheny K, Tsai YY, Chen WV, Shete S, Spitz MR, Houlston RS. Genome-wide association scan of tag SNPs identifies a susceptibility locus for lung cancer at 15q25.1. Nat Genet. 2008;40:616–622. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aoshiba K, Nagai A, Yasui S, Konno K. Nicotine prolongs neutrophil survival by suppressing apoptosis. J Lab Clin Med. 1996;127:186–194. - PubMed
-
- Arredondo J, Hall LL, Ndoye A, Nguyen VT, Chernyavsky AI, Bercovich D, Orr-Urtreger A, Beaudet AL, Grando SA. Central role of fibroblast alpha3 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in mediating cutaneous effects of nicotine. Lab Invest. 2003;83:207–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

