The guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) Ect2 is an oncogene in human cancer
- PMID: 19896966
- PMCID: PMC2863999
- DOI: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2009.10.010
The guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) Ect2 is an oncogene in human cancer
Figures

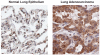
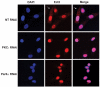
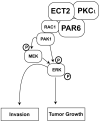
References
-
- Balsara BR, Sonoda G, du Manoir S, Siegfried JM, Gabrielson E, Testa JR. Comparative genomic hybridization analysis detects frequent, often high-level, overrepresentation of DNA sequences at 3q, 5p, 7p, and 8q in human non-small cell lung carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1997;57:2116–2120. - PubMed
-
- Bork P, Hofmann K, Bucher P, Neuwald AF, Altschul SF, Koonin EV. A superfamily of conserved domains in DNA damage-responsive cell cycle checkpoint proteins. Faseb J. 1997;11:68–76. - PubMed
-
- Brass N, Ukena I, Remberger K, Mack U, Sybrecht GW, Meese EU. DNA amplification on chromosome 3q26.1-q26.3 in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung detected by reverse chromosome painting. Eur J Cancer. 1996;32A:1205–1208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

