Aminoquinoline surfen inhibits the action of SEVI (semen-derived enhancer of viral infection)
- PMID: 19897482
- PMCID: PMC2804344
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.066167
Aminoquinoline surfen inhibits the action of SEVI (semen-derived enhancer of viral infection)
Abstract
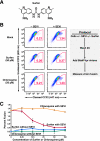
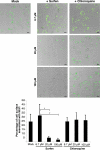
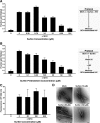
In semen, proteolytic peptide fragments from prostatic acid phosphatase can form amyloid fibrils termed SEVI (semen-derived enhancer of viral infection). These fibrils greatly enhance human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infectivity by increasing the attachment of virions to target cells. Therefore, SEVI may have a significant impact on whether HIV is successfully transmitted during sexual contact. Here, we demonstrate that surfen, a small molecule heparan sulfate proteoglycan antagonist, inhibits both SEVI- and semen-mediated enhancement of HIV type 1 infection. Surfen interferes with the binding of SEVI to both target cells and HIV type 1 virions but does not deaggregate SEVI fibrils. Because SEVI can increase HIV infectivity by several orders of magnitude, supplementing current HIV microbicide candidates with SEVI inhibitors, such as surfen, might greatly increase their potency.
Figures


References
-
- Münch J., Rücker E., Ständker L., Adermann K., Goffinet C., Schindler M., Wildum S., Chinnadurai R., Rajan D., Specht A., Giménez-Gallego G., Sánchez P. C., Fowler D. M., Koulov A., Kelly J. W., Mothes W., Grivel J. C., Margolis L., Keppler O. T., Forssmann W. G., Kirchhoff F. (2007) Cell 131, 1059–1071 - PubMed
-
- Rönnberg L., Vihko P., Sajanti E., Vihko R. (1981) Int. J. Androl. 4, 372–378 - PubMed
-
- Toyoshima K., Vogt P. K. (1969) Virology 38, 414–426 - PubMed
-
- Umber F., Stoerring F. K., Foellmer W. (1938) Klinische Wochenschrift. 17, 443–446
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

