Synovial fibroblasts spread rheumatoid arthritis to unaffected joints
- PMID: 19898488
- PMCID: PMC3678354
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2050
Synovial fibroblasts spread rheumatoid arthritis to unaffected joints
Abstract
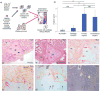
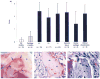
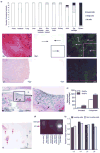
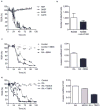
Active rheumatoid arthritis originates from few joints but subsequently affects the majority of joints. Thus far, the pathways of the progression of the disease are largely unknown. As rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts (RASFs) which can be found in RA synovium are key players in joint destruction and are able to migrate in vitro, we evaluated the potential of RASFs to spread the disease in vivo. To simulate the primary joint of origin, we implanted healthy human cartilage together with RASFs subcutaneously into severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mice. At the contralateral flank, we implanted healthy cartilage without cells. RASFs showed an active movement to the naive cartilage via the vasculature independent of the site of application of RASFs into the SCID mouse, leading to a marked destruction of the target cartilage. These findings support the hypothesis that the characteristic clinical phenomenon of destructive arthritis spreading between joints is mediated, at least in part, by the transmigration of activated RASFs.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Karouzakis E, Neidhart M, Gay RE, Gay S. Molecular and cellular basis of rheumatoid joint destruction. Immunol Lett. 2006;106:8–13. - PubMed
-
- Muller-Ladner U, Pap T, Gay RE, Neidhart M, Gay S. Mechanisms of disease: the molecular and cellular basis of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2005;1:102–10. - PubMed
-
- Looney RJ. B cell-targeted therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: an update on the evidence. Drugs. 2006;66:625–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

