Direct cell reprogramming is a stochastic process amenable to acceleration
- PMID: 19898493
- PMCID: PMC2789972
- DOI: 10.1038/nature08592
Direct cell reprogramming is a stochastic process amenable to acceleration
Abstract
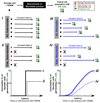
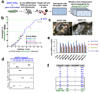
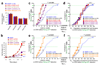
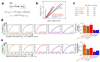
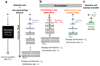
Direct reprogramming of somatic cells into induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells can be achieved by overexpression of Oct4, Sox2, Klf4 and c-Myc transcription factors, but only a minority of donor somatic cells can be reprogrammed to pluripotency. Here we demonstrate that reprogramming by these transcription factors is a continuous stochastic process where almost all mouse donor cells eventually give rise to iPS cells on continued growth and transcription factor expression. Additional inhibition of the p53/p21 pathway or overexpression of Lin28 increased the cell division rate and resulted in an accelerated kinetics of iPS cell formation that was directly proportional to the increase in cell proliferation. In contrast, Nanog overexpression accelerated reprogramming in a predominantly cell-division-rate-independent manner. Quantitative analyses define distinct cell-division-rate-dependent and -independent modes for accelerating the stochastic course of reprogramming, and suggest that the number of cell divisions is a key parameter driving epigenetic reprogramming to pluripotency.
Figures
References
-
- Hanna J, et al. Treatment of sickle cell anemia mouse model with iPS cells generated from autologous skin. Science. 2007;318(5858):1920–1923. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, et al. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell. 2007;131(5):861–872. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell. 2006;126(4):663–676. - PubMed
-
- Wernig M, et al. In vitro reprogramming of fibroblasts into a pluripotent ES-cell-like state. Nature. 2007;448(7151):318–324. - PubMed
-
- Yu J, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cell lines derived from human somatic cells. Science. 2007;318(5858):1917–1920. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

