Loss of hepatocyte-nuclear-factor-4alpha affects colonic ion transport and causes chronic inflammation resembling inflammatory bowel disease in mice
- PMID: 19898610
- PMCID: PMC2764139
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007609
Loss of hepatocyte-nuclear-factor-4alpha affects colonic ion transport and causes chronic inflammation resembling inflammatory bowel disease in mice
Abstract
Background: Hnf4alpha, an epithelial specific transcriptional regulator, is decreased in inflammatory bowel disease and protects against chemically-induced colitis in mice. However, the precise role of this factor in maintaining normal inflammatory homeostasis of the intestine remains unclear. The aim of this study was to evaluate the sole role of epithelial Hnf4alpha in the maintenance of gut inflammatory homeostasis in mice.
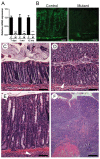
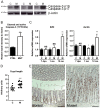
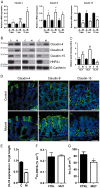
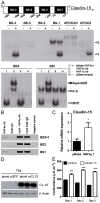
Methodology/principal findings: We show here that specific epithelial deletion of Hnf4alpha in mice causes spontaneous chronic intestinal inflammation leading to focal areas of crypt dropout, increased cytokines and chemokines secretion, immune cell infiltrates and crypt hyperplasia. A gene profiling analysis in diseased Hnf4alpha null colon confirms profound genetic changes in cell death and proliferative behaviour related to cancer. Among the genes involved in the immune protection through epithelial barrier function, we identify the ion transporter claudin-15 to be down-modulated early in the colon of Hnf4alpha mutants. This coincides with a significant decrease of mucosal ion transport but not of barrier permeability in young animals prior to the manifestation of the disease. We confirm that claudin-15 is a direct Hnf4alpha gene target in the intestinal epithelial context and is down-modulated in mouse experimental colitis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Conclusion: Our results highlight the critical role of Hnf4alpha to maintain intestinal inflammatory homeostasis during mouse adult life and uncover a novel function for Hnf4alpha in the regulation of claudin-15 expression. This establishes Hnf4alpha as a mediator of ion epithelial transport, an important process for the maintenance of gut inflammatory homeostasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha in the intestinal epithelial cells protects against inflammatory bowel disease.Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008 Jul;14(7):908-20. doi: 10.1002/ibd.20413. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2008. PMID: 18338782 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha contributes to an intestinal epithelial phenotype in vitro and plays a partial role in mouse intestinal epithelium differentiation.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009 Jul;297(1):G124-34. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.90690.2008. Epub 2009 Apr 23. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19389805
-
Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha promotes gut neoplasia in mice and protects against the production of reactive oxygen species.Cancer Res. 2010 Nov 15;70(22):9423-33. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-1697. Epub 2010 Nov 9. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 21062980
-
Inverse regulation of claudin-2 and -7 expression by p53 and hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α in colonic MCE301 cells.Tissue Barriers. 2021 Jan 2;9(1):1860409. doi: 10.1080/21688370.2020.1860409. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Tissue Barriers. 2021. PMID: 33356822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development, validation and implementation of an in vitro model for the study of metabolic and immune function in normal and inflamed human colonic epithelium.Dan Med J. 2015 Jan;62(1):B4973. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25557335 Review.
Cited by
-
Conserved roles for Hnf4 family transcription factors in zebrafish development and intestinal function.Genetics. 2022 Nov 30;222(4):iyac133. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyac133. Genetics. 2022. PMID: 36218393 Free PMC article.
-
Human Intestinal Barrier Function in Health and Disease.Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2016 Oct 20;7(10):e196. doi: 10.1038/ctg.2016.54. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27763627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opposing roles of nuclear receptor HNF4α isoforms in colitis and colitis-associated colon cancer.Elife. 2016 May 11;5:e10903. doi: 10.7554/eLife.10903. Elife. 2016. PMID: 27166517 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Effects of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4α Isoforms on Tumor Growth and T-Cell Factor 4/AP-1 Interactions in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;35(20):3471-90. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00030-15. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Mol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26240283 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor HNF4α binding sequences are widespread in Alu repeats.BMC Genomics. 2011 Nov 15;12:560. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-560. BMC Genomics. 2011. PMID: 22085832 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen WS, Manova K, Weinstein DC, Duncan SA, Plump AS, et al. Disruption of the HNF-4 gene, expressed in visceral endoderm, leads to cell death in embryonic ectoderm and impaired gastrulation of mouse embryos. Genes Dev. 1994;8:2466–2477. - PubMed
-
- Parviz F, Matullo C, Garrison WD, Savatski L, Adamson JW, et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha controls the development of a hepatic epithelium and liver morphogenesis. Nat Genet. 2003;34:292–296. - PubMed
-
- Lussier CR, Babeu JP, Auclair BA, Perreault N, Boudreau F. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4alpha promotes differentiation of intestinal epithelial cells in a coculture system. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2008;294:G418–428. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

