Cardiac conduction system: delineation of anatomic landmarks with multidetector CT
- PMID: 19898655
- PMCID: PMC2766580
Cardiac conduction system: delineation of anatomic landmarks with multidetector CT
Abstract
Major components of the cardiac conduction system including the sinoatrial node (SAN), atrioventricular node (AVN), the His Bundle, and the right and left bundle branches are too small to be directly visualized by multidetector CT (MDCT) given the limited spatial resolution of current scanners. However, the related anatomic landmarks and variants of this system a well as the areas with special interest to electrophysiologists can be reliably demonstrated by MDCT. Some of these structures and landmarks include the right SAN artery, right atrial cavotricuspid isthmus, Koch triangle, AVN artery, interatrial muscle bundles, and pulmonary veins. In addition, MDCT has an imperative role in demarcating potential arrhythmogenic structures. The aim of this review will be to assess the extent at which MDCT can outline the described anatomic landmarks and therefore provide crucial information used in clinical practice.
Keywords: Cardiac Conduction System; Delineation of Anatomic Landmarks; Multidetector CT.
Figures

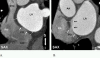






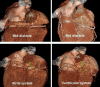


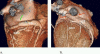

Similar articles
-
Septal Atrioventricular Junction Region: Comprehensive Imaging in Adults.Radiographics. 2016 Nov-Dec;36(7):1966-1986. doi: 10.1148/rg.2016160010. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Radiographics. 2016. PMID: 27740897 Review.
-
Arterial supply to sinuatrial and atrioventricular nodes: imaging with multidetector CT.Radiology. 2008 Jan;246(1):99-107; discussion 108-9. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2461070030. Epub 2007 Nov 16. Radiology. 2008. PMID: 18024438
-
Molecular characterization of the ventricular conduction system in the developing mouse heart: topographical correlation in normal and congenitally malformed hearts.Cardiovasc Res. 2001 Feb 1;49(2):417-29. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(00)00252-2. Cardiovasc Res. 2001. PMID: 11164852
-
Re-evaluation of the structure of the atrioventricular node and its connections with the atrium.Europace. 2020 May 1;22(5):821-830. doi: 10.1093/europace/euaa031. Europace. 2020. PMID: 32304217
-
Cardiac conduction system: anatomic landmarks relevant to interventional electrophysiologic techniques demonstrated with 64-detector CT.Radiographics. 2007 Nov-Dec;27(6):1539-65; discussion 1566-7. doi: 10.1148/rg.276075003. Radiographics. 2007. PMID: 18025502 Review.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Coronary Sinus Pacing for Cardiogenic Shock Due to Percutaneous Coronary Intervention-induced Sick Sinus Syndrome: Two Case Reports.Intern Med. 2023 Nov 15;62(22):3355-3360. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1527-22. Epub 2023 Mar 31. Intern Med. 2023. PMID: 37005264 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac dose in the treatment of synchronous bilateral breast cancer patients between three different radiotherapy techniques (VMAT, IMRT, and 3D CRT).Discov Oncol. 2023 Mar 2;14(1):29. doi: 10.1007/s12672-023-00636-z. Discov Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36862205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanchez-Quintana D, et al. Anatomy of cardiac nodes and atrioventricular specialized conduction system. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2003;56:1085. - PubMed
-
- Malouf JF, et al. Functional anatomy of the heart. In: Fuster V, et al., editors. The heart. 11th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2004. p. 75.
-
- Ho SY, et al. Atrial structure and fibres: morphologic bases of atrial conduction. Cardiovasc Res. 2002;54:325. - PubMed
-
- Anderson RH, et al. The anatomy of the heart revisited. Anat Rec. 1996;246:1. - PubMed
-
- Edwards WD. Applied anatomy of the heart. In: Giuliani ER, et al., editors. Cardiology: fundamentals and practice, 2nd ed. St. Louis: St. Louis; 1991. p. 47 .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
