Word learning in children with autism spectrum disorders
- PMID: 19899931
- PMCID: PMC3035482
- DOI: 10.1037/a0016223
Word learning in children with autism spectrum disorders
Abstract
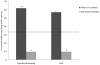
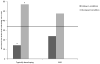
Autism spectrum disorders (ASD) have been gaining attention, partly as an example of unusual developmental trajectories related to early neurobiological differences. The present investigation addressed the process of learning new words to explore mechanisms of language delay and impairment. The sample included 21 typically developing toddlers matched on expressive vocabulary with 21 young children with ASD. Two tasks were administered to teach children a new word and were supplemented by cognitive and diagnostic measures. In most analyses, there were no group differences in performance. Children with ASD did not consistently make mapping errors, even in word learning situations that required the use of social information. These findings indicate that some children with ASD, in developmentally appropriate tasks, are able to use information from social interactions to guide word-object mappings. This result has important implications for understanding of how children with ASD learn language.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Fourth. Washington, DC: Author; 1994.
-
- Anderson DK, Lord C, Risi S, Shulman C, Welch K, DiLavore PS, et al. Patterns of growth in verbal abilities among children with autism spectrum disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 2007;75(4):594–604. - PubMed
-
- Bailey A, Phillips W, Rutter M. Autism: Towards an integration of clinical, genetic, neuropsychological, and neurobiological perspectives. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 1996;37:89–126. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin D. Infants' contribution to the achievement of joint reference. Child Development. 1991;62(5):875–890. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin D. Infants' ability to consult the speaker for clues to word reference. Journal of Child Language. 1993;20:395–418. - PubMed

