F-actin structure destabilization and DNase I binding loop: fluctuations mutational cross-linking and electron microscopy analysis of loop states and effects on F-actin
- PMID: 19900461
- PMCID: PMC3070609
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.11.001
F-actin structure destabilization and DNase I binding loop: fluctuations mutational cross-linking and electron microscopy analysis of loop states and effects on F-actin
Abstract
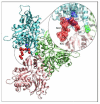
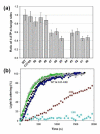
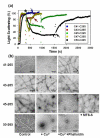
The conformational dynamics of filamentous actin (F-actin) is essential for the regulation and functions of cellular actin networks. The main contribution to F-actin dynamics and its multiple conformational states arises from the mobility and flexibility of the DNase I binding loop (D-loop; residues 40-50) on subdomain 2. Therefore, we explored the structural constraints on D-loop plasticity at the F-actin interprotomer space by probing its dynamic interactions with the hydrophobic loop (H-loop), the C-terminus, and the W-loop via mutational disulfide cross-linking. To this end, residues of the D-loop were mutated to cysteines on yeast actin with a C374A background. These mutants showed no major changes in their polymerization and nucleotide exchange properties compared to wild-type actin. Copper-catalyzed disulfide cross-linking was investigated in equimolar copolymers of cysteine mutants from the D-loop with either wild-type (C374) actin or mutant S265C/C374A (on the H-loop) or mutant F169C/C374A (on the W-loop). Remarkably, all tested residues of the D-loop could be cross-linked to residues 374, 265, and 169 by disulfide bonds, demonstrating the plasticity of the interprotomer region. However, each cross-link resulted in different effects on the filament structure, as detected by electron microscopy and light-scattering measurements. Disulfide cross-linking in the longitudinal orientation produced mostly no visible changes in filament morphology, whereas the cross-linking of D-loop residues >45 to the H-loop, in the lateral direction, resulted in filament disruption and the presence of amorphous aggregates on electron microscopy images. A similar aggregation was also observed upon cross-linking the residues of the D-loop (>41) to residue 169. The effects of disulfide cross-links on F-actin stability were only partially accounted for by the simulations of current F-actin models. Thus, our results present evidence for the high level of conformational plasticity in the interprotomer space and document the link between D-loop interactions and F-actin stability.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Kabsch W, Mannherz HG, Suck D, Pai EF, Holmes KC. Atomic structure of the actin:DNase I complex. Nature. 1990;347:37–44. - PubMed
-
- Tirion MM, ben-Avraham D. Normal mode analysis of G-actin. J Mol Biol. 1993;230:186–95. - PubMed
-
- Graceffa P, Dominguez R. Crystal structure of monomeric actin in the ATP state. Structural basis of nucleotide-dependent actin dynamics. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:34172–80. - PubMed
-
- McLaughlin PJ, Gooch JT, Mannherz HG, Weeds AG. Structure of gelsolin segment 1-actin complex and the mechanism of filament severing. Nature. 1993;364:685–92. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

