Ultrasound-triggered release of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator from echogenic liposomes
- PMID: 19900755
- PMCID: PMC3037723
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2009.08.009
Ultrasound-triggered release of recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator from echogenic liposomes
Abstract
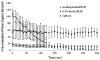
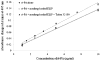
Echogenic liposomes (ELIP) were developed as ultrasound-triggered targeted drug or gene delivery vehicles (Lanza et al. 1997; Huang et al. 2001). Recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator (rt-PA), a thrombolytic, has been loaded into ELIP (Tiukinhoy-Laing et al. 2007). These vesicles have the potential to be used for ultrasound-enhanced thrombolysis in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke, myocardial infarction, deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolus. A clinical diagnostic ultrasound scanner (Philips HDI 5000; Philips Medical Systems, Bothell, WA, USA) equipped with a linear array transducer (L12-5) was employed for in vitro studies using rt-PA-loaded ELIP (T-ELIP). The goal of this study was to quantify ultrasound-triggered drug release from rt-PA-loaded echogenic liposomes. T-ELIP samples were exposed to 6.9-MHz B-mode pulses at a low pressure amplitude (600 kPa) to track the echogenicity over time under four experimental conditions: (1) flow alone to monitor gas diffusion from the T-ELIP, (2) pulsed 6.0-MHz color Doppler exposure above the acoustically driven threshold (0.8 MPa) to force gas out of the liposome gently, (3) pulsed 6.0-MHz color Doppler above the rapid fragmentation threshold (2.6 MPa) or (4) Triton X-100 to rupture the T-ELIP chemically as a positive control. Release of rt-PA for each ultrasound exposure protocol was assayed spectrophotometrically. T-ELIP were echogenic in the flow model (5 mL/min) for 30 min. The thrombolytic drug remained associated with the liposome when exposed to low-amplitude B-mode pulses over 60 min and was released when exposed to color Doppler pulses or Triton X-100. The rt-PA released from the liposomes had similar enzymatic activity as the free drug. These T-ELIP are robust and echogenic during continuous fundamental 6.9-MHz B-mode imaging at a low exposure output level (600 kPa). Furthermore, a therapeutic concentration of rt-PA can be released by fragmenting the T-ELIP with pulsed 6.0-MHz color Doppler ultrasound above the rapid fragmentation threshold (1.59 MPa). (E-mail: denise.smith@uc.edu).
Figures






References
-
- Alexandrov AV. Ultrasound enhanced thrombolysis for stroke. Seminars in Cerebrovascular Diseases and Stroke. 2006;5:106–110.
-
- Apfel RE, Holland CK. Gauging the likelihood of cavitation from short-pulse, low-duty cycle diagnostic ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1991;17:179–185. - PubMed
-
- Bevan DP, Karshafian R, Burns PN. The influence of fragmentation on the acoustic response from shrinking bubbles. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2008;34 (7):1152–1162. - PubMed
-
- Bouakaz A, de Jong N. WFUMB safety symposium on echo-contrast agents: Nature and types of ultrasound contrast agents. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2007;33:187–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

