Plasma interleukin-1beta concentration is associated with stroke in sickle cell disease
- PMID: 19900820
- PMCID: PMC2808442
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cyto.2009.10.002
Plasma interleukin-1beta concentration is associated with stroke in sickle cell disease
Abstract
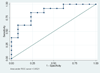
The pathogenesis of sickle cell disease (HbSS), which has numerous complications including stroke, involves inflammation resulting in alteration of plasma inflammatory protein concentration. We investigated HbSS children with abnormal cerebral blood flow detected by trans-cranial Doppler ultrasound (TCD) who participated in the multi-center stroke prevention (STOP) study, to determine if plasma inflammatory protein concentration is associated with the outcome of stroke. Thirty-nine plasma samples from HbSS participants with elevated TCD who had no stroke, HbSS-NS (n=13) or had stroke, HbSS-S (n=13), HbSS steady-state controls (n=7) and controls with normal hemoglobin, HbAA (n=6), were analyzed simultaneously for 27 circulating inflammatory proteins. Logistic regression and receiver operating characteristics curve analysis of stroke on plasma inflammatory mediator concentration, adjusted for age and gender, demonstrated that interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) was protective against stroke development (HbSS-NS=19, 17-23, HbSS-S=17, 16-19 pg/mL, median and 25th-75th percentile; odds ratio=0.59, C.I.=0.36-0.96) and was a good predictor of stroke (area under curve=0.852). This result demonstrates a strong association of systemic inflammation with stroke development in HbSS via moderately increased plasma IL-1beta concentration, which is furthermore associated with a decreased likelihood of stroke in HbSS.
Copyright 2009 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54 MD007588/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R25 RR017694/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G12 RR003034/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR011104/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20-RR11104/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 RR026137/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- RR033062/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5R90HG004151-03/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- S06 GM008248/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM058268/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- G12-RR03034/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R90 HG004151/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

