The MiST2 database: a comprehensive genomics resource on microbial signal transduction
- PMID: 19900966
- PMCID: PMC2808908
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp940
The MiST2 database: a comprehensive genomics resource on microbial signal transduction
Abstract
The MiST2 database (http://mistdb.com) identifies and catalogs the repertoire of signal transduction proteins in microbial genomes. Signal transduction systems regulate the majority of cellular activities including the metabolism, development, host-recognition, biofilm production, virulence, and antibiotic resistance of human pathogens. Thus, knowledge of the proteins and interactions that comprise these communication networks is an essential component to furthering biomedical discovery. These are identified by searching protein sequences for specific domain profiles that implicate a protein in signal transduction. Compared to the previous version of the database, MiST2 contains a host of new features and improvements including the following: draft genomes; extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factor protein identification; enhanced classification of signaling proteins; novel, high-quality domain models for identifying histidine kinases and response regulators; neighboring two-component genes; gene cart; better search capabilities; enhanced taxonomy browser; advanced genome browser; and a modern, biologist-friendly web interface. MiST2 currently contains 966 complete and 157 draft bacterial and archaeal genomes, which collectively contain more than 245 000 signal transduction proteins. The majority (66%) of these are one-component systems, followed by two-component proteins (26%), chemotaxis (6%), and finally ECF factors (2%).
Figures
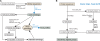
References
-
- Stock AM, Robinson VL, Goudreau PN. Two-component signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000;69:183–215. - PubMed
-
- Hengge R. Principles of c-di-GMP signalling in bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2009;7:263–273. - PubMed
-
- Wadhams GH, Armitage JP. Making sense of it all: bacterial chemotaxis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004;5:1024–1037. - PubMed

