YybT is a signaling protein that contains a cyclic dinucleotide phosphodiesterase domain and a GGDEF domain with ATPase activity
- PMID: 19901023
- PMCID: PMC2804195
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.040238
YybT is a signaling protein that contains a cyclic dinucleotide phosphodiesterase domain and a GGDEF domain with ATPase activity
Erratum in
- J Biol Chem. 2011 Aug 19;286(33):29441
Abstract
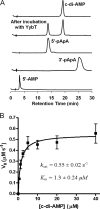
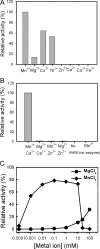
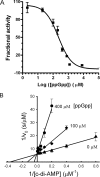
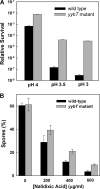
The cyclic dinucleotide c-di-AMP [corrected] synthesized by the diadenylate cyclase domain was discovered recently [corrected] as a messenger molecule for signaling DNA breaks in Bacillus subtilis. By searching bacterial genomes, we identified a family of DHH/DHHA1 domain proteins (COG3387) that co-occur with a subset of the diadenylate cyclase domain proteins. Here we report that the B. subtilis protein YybT, a member of the COG3387 family proteins, exhibits phosphodiesterase activity toward cyclic dinucleotides. The DHH/DHHA1 domain hydrolyzes c-di-AMP and c-di-GMP to generate the linear dinucleotides 5'-pApA and 5'-pGpG. The data suggest that c-di-AMP could be the physiological substrate for YybT given the physiologically relevant Michaelis-Menten constant (K(m)) and the presence of YybT family proteins in the bacteria lacking c-di-GMP signaling network. The bacterial regulator ppGpp was found to be a strong competitive inhibitor of the DHH/DHHA1 domain, suggesting that YybT is under tight control during stringent response. In addition, the atypical GGDEF domain of YybT exhibits unexpected ATPase activity, distinct from the common diguanylate cyclase activity for GGDEF domains. We further demonstrate the participation of YybT in DNA damage and acid resistance by characterizing the phenotypes of the DeltayybT mutant. The novel enzymatic activity and stress resistance together point toward a role for YybT in stress signaling and response.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Structural and biochemical characterization of the catalytic domains of GdpP reveals a unified hydrolysis mechanism for the DHH/DHHA1 phosphodiesterase.Biochem J. 2018 Jan 5;475(1):191-205. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170739. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 29203646
-
New Insights into the Cyclic Di-adenosine Monophosphate (c-di-AMP) Degradation Pathway and the Requirement of the Cyclic Dinucleotide for Acid Stress Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus.J Biol Chem. 2016 Dec 30;291(53):26970-26986. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.747709. Epub 2016 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27834680 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Phosphodiesterase of the GdpP Family Modulates Cyclic di-AMP Levels in Response to Cell Membrane Stress in Daptomycin-Resistant Enterococci.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Feb 23;61(3):e01422-16. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01422-16. Print 2017 Mar. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017. PMID: 28069645 Free PMC article.
-
Making and Breaking of an Essential Poison: the Cyclases and Phosphodiesterases That Produce and Degrade the Essential Second Messenger Cyclic di-AMP in Bacteria.J Bacteriol. 2018 Dec 7;201(1):e00462-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00462-18. Print 2019 Jan 1. J Bacteriol. 2018. PMID: 30224435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress in Understanding the Molecular Basis Underlying Functional Diversification of Cyclic Dinucleotide Turnover Proteins.J Bacteriol. 2017 Feb 14;199(5):e00790-16. doi: 10.1128/JB.00790-16. Print 2017 Mar 1. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 28031279 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Rv3586 (DacA) is a diadenylate cyclase that converts ATP or ADP into c-di-AMP.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35206. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035206. Epub 2012 Apr 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22529992 Free PMC article.
-
The Characterization of Escherichia coli CpdB as a Recombinant Protein Reveals that, besides Having the Expected 3´-Nucleotidase and 2´,3´-Cyclic Mononucleotide Phosphodiesterase Activities, It Is Also Active as Cyclic Dinucleotide Phosphodiesterase.PLoS One. 2016 Jun 13;11(6):e0157308. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157308. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27294396 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Levels of (p)ppGpp Correlate with Virulence and Biofilm Formation, but Not with Growth, in Strains of Uropathogenic Escherichia coli.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 7;24(4):3315. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043315. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834725 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of function of the gdpP protein leads to joint β-lactam/glycopeptide tolerance in Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012 Jan;56(1):579-81. doi: 10.1128/AAC.05148-11. Epub 2011 Oct 10. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012. PMID: 21986827 Free PMC article.
-
The Many Roles of the Bacterial Second Messenger Cyclic di-AMP in Adapting to Stress Cues.J Bacteriol. 2020 Dec 7;203(1):e00348-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00348-20. Print 2020 Dec 7. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32839175 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Römling U., Gomelsky M., Galperin M. Y. (2005) Mol. Microbiol. 57, 629–639 - PubMed
-
- Hengge R. (2009) Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7, 263–273 - PubMed
-
- Galperin M. Y., Nikolskaya A. N., Koonin E. V. (2001) FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 203, 11–21 - PubMed
-
- Bejerano-Sagie M., Oppenheimer-Shaanan Y., Berlatzky I., Rouvinski A., Meyerovich M., Ben-Yehuda S. (2006) Cell 125, 679–690 - PubMed
-
- Witte G., Hartung S., Büttner K., Hopfner K. P. (2008) Mol. Cell 30, 167–178 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

