CUCU modification of mRNA promotes decapping and transcript degradation in Aspergillus nidulans
- PMID: 19901075
- PMCID: PMC2798463
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00997-09
CUCU modification of mRNA promotes decapping and transcript degradation in Aspergillus nidulans
Abstract
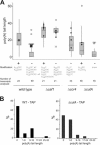
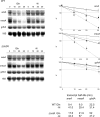
In eukaryotes, mRNA decay is generally initiated by the shortening of the poly(A) tail mediated by the major deadenylase complex Ccr4-Caf1-Not. The deadenylated transcript is then rapidly degraded, primarily via the decapping-dependent pathway. Here we report that in Aspergillus nidulans both the Caf1 and Ccr4 orthologues are functionally distinct deadenylases in vivo: Caf1 is required for the regulated degradation of specific transcripts, and Ccr4 is responsible for basal degradation. Intriguingly disruption of the Ccr4-Caf1-Not complex leads to deadenylation-independent decapping. Additionally, decapping is correlated with a novel transcript modification, addition of a CUCU sequence. A member of the nucleotidyltransferase superfamily, CutA, is required for this modification, and its disruption leads to a reduced rate of decapping and subsequent transcript degradation. We propose that 3' modification of adenylated mRNA, which is likely to represent a common eukaryotic process, primes the transcript for decapping and efficient degradation.
Figures



References
-
- Aebi, M., G. Kirchner, J. Y. Chen, U. Vijayraghavan, A. Jacobson, N. C. Martin, and J. Abelson. 1990. Isolation of a temperature-sensitive mutant with an altered tRNA nucleotidyltransferase and cloning of the gene encoding tRNA nucleotidyltransferase in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 265:16216-16220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
