Impact of Y143 HIV-1 integrase mutations on resistance to raltegravir in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 19901095
- PMCID: PMC2798554
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01075-09
Impact of Y143 HIV-1 integrase mutations on resistance to raltegravir in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
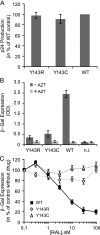
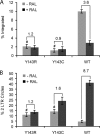
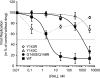
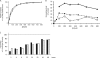
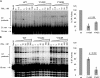
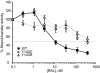
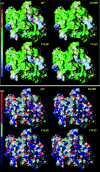
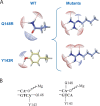
Integrase (IN), the HIV-1 enzyme responsible for the integration of the viral genome into the chromosomes of infected cells, is the target of the recently approved antiviral raltegravir (RAL). Despite this drug's activity against viruses resistant to other antiretrovirals, failures of raltegravir therapy were observed, in association with the emergence of resistance due to mutations in the integrase coding region. Two pathways involving primary mutations on residues N155 and Q148 have been characterized. It was suggested that mutations at residue Y143 might constitute a third primary pathway for resistance. The aims of this study were to investigate the susceptibility of HIV-1 Y143R/C mutants to raltegravir and to determine the effects of these mutations on the IN-mediated reactions. Our observations demonstrate that Y143R/C mutants are strongly impaired for both of these activities in vitro. However, Y143R/C activity can be kinetically restored, thereby reproducing the effect of the secondary G140S mutation that rescues the defect associated with the Q148R/H mutants. A molecular modeling study confirmed that Y143R/C mutations play a role similar to that determined for Q148R/H mutations. In the viral replicative context, this defect leads to a partial block of integration responsible for a weak replicative capacity. Nevertheless, the Y143 mutant presented a high level of resistance to raltegravir. Furthermore, the 50% effective concentration (EC(50)) determined for Y143R/C mutants was significantly higher than that obtained with G140S/Q148R mutants. Altogether our results not only show that the mutation at position Y143 is one of the mechanisms conferring resistance to RAL but also explain the delayed emergence of this mutation.
Figures
References
-
- Agapkina, J., M. Smolov, S. Barbe, E. Zubin, T. Zatsepin, E. Deprez, B. M. Le, J. F. Mouscadet, and M. Gottikh. 2006. Probing of HIV-1 integrase-DNA interactions using novel analogs of viral DNA. J. Biol. Chem. 281:11530-11540. - PubMed
-
- Brown, P. O. 1990. Integration of retroviral DNA. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 157:19-48. - PubMed
-
- Brussel, A., O. Delelis, and P. Sonigo. 2005. Alu-LTR real-time nested PCR assay for quantifying integrated HIV-1 DNA. Methods Mol. Biol. 304:139-154. - PubMed
-
- Ceccherini-Silberstein, F., I. Malet, R. D'Arrigo, A. Antinori, A. G. Marcelin, and C. F. Perno. 2009. Characterization and structural analysis of HIV-1 integrase conservation. AIDS Rev. 11:17-29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

