Androgen-induced Rhox homeobox genes modulate the expression of AR-regulated genes
- PMID: 19901196
- PMCID: PMC2802895
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0303
Androgen-induced Rhox homeobox genes modulate the expression of AR-regulated genes
Abstract
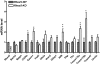
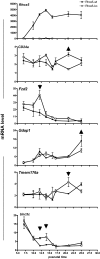
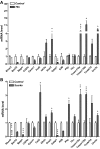
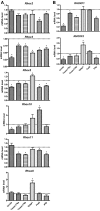
Rhox5, the founding member of the reproductive homeobox on the X chromosome (Rhox) gene cluster, encodes a homeodomain-containing transcription factor that is selectively expressed in Sertoli cells, where it promotes the survival of male germ cells. To identify Rhox5-regulated genes, we generated 15P-1 Sertoli cell clones expressing physiological levels of Rhox5 from a stably transfected expression vector. Microarray analysis identified many genes altered in expression in response to Rhox5, including those encoding proteins controlling cell cycle regulation, apoptosis, metabolism, and cell-cell interactions. Fifteen of these Rhox5-regulated genes were chosen for further analysis. Analysis of Rhox5-null male mice indicated that at least nine of these are Rhox5-regulated in the testes in vivo. Many of them have distinct postnatal expression patterns and are regulated by Rhox5 at different postnatal time points. Most of them are expressed in Sertoli cells, indicating that they are candidates to be directly regulated by Rhox5. Transfection analysis with expression vectors encoding different mouse and human Rhox family members revealed that the regulatory response of a subset of these Rhox5-regulated genes is both conserved and redundant. Given that Rhox5 depends on androgen receptor (AR) for expression in Sertoli cells, we examined whether some Rhox5-regulated genes are also regulated by AR. We provide several lines of evidence that this is the case, leading us to propose that RHOX5 serves as a key intermediate transcription factor that directs some of the actions of AR in the testes.
Figures



References
-
- Ingham PW, Martinez Arias A 1992 Boundaries and fields in early embryos. Cell 68:221–235 - PubMed
-
- Chiba S 1998 Homeobox genes in normal hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis. Int J Hematol 68:343–353 - PubMed
-
- Awgulewitsch A 2003 Hox in hair growth and development. Naturwissenschaften 90:193–211 - PubMed
-
- Lee CS, Kaestner KH 2004 Clinical endocrinology and metabolism. Development of gut endocrine cells. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 18:453–462 - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm D, Palmer S, Koopman P 2007 Sex determination and gonadal development in mammals. Physiol Rev 87:1–28 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

