Rescue of radiation-induced cognitive impairment through cranial transplantation of human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 19901336
- PMCID: PMC2776427
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0909293106
Rescue of radiation-induced cognitive impairment through cranial transplantation of human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
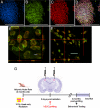
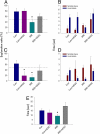
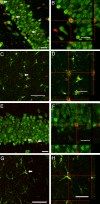
Cranial irradiation remains a frontline treatment for the control of tumor growth, and individuals surviving such treatments often manifest various degrees of cognitive dysfunction. Radiation-induced depletion of stem/precursor cell pools in the brain, particularly those residing in the neurogenic region of the hippocampus, is believed, in part, to be responsible for these often-unavoidable cognitive deficits. To explore the possibility of ameliorating radiation-induced cognitive impairment, athymic nude rats subjected to head only irradiation (10 Gy) were transplanted 2 days afterward with human embryonic stem cells (hESC) into the hippocampal formation and analyzed for stem cell survival, differentiation, and cognitive function. Animals receiving hESC transplantation exhibited superior performance on a hippocampal-dependent cognitive task 4 months postirradiation, compared to their irradiated surgical counterparts that did not receive hESCs. Significant stem cell survival was found at 1 and 4 months postirradiation, and transplanted cells showed robust migration to the subgranular zone throughout the dentate gyrus, exhibiting signs of neuron morphology within this neurogenic niche. These results demonstrate the capability to ameliorate radiation-induced normal tissue injury using hESCs, and suggest that such strategies may provide useful interventions for reducing the adverse effects of irradiation on cognition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Walker MD, Strike TA, Sheline GE. An analysis of dose-effect relationship in the radiotherapy of malignant gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1979;5:1725–1731. - PubMed
-
- Sheline GE, Wara WM, Smith V. Therapeutic irradiation and brain injury. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1980;6:1215–1228. - PubMed
-
- Tofilon PJ, Fike JR. The radioresponse of the central nervous system: A dynamic process. Radiat Res. 2000;153:357–370. - PubMed
-
- Shaw E, et al. Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: Final report of RTOG protocol 90–05. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2000;47:291–298. - PubMed
-
- Butler J, Rapp S, Shaw E. Managing the cognitive effects of brain tumor radiation therapy. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2006;7:517–523. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

