A t-butyloxycarbonyl-modified Wnt5a-derived hexapeptide functions as a potent antagonist of Wnt5a-dependent melanoma cell invasion
- PMID: 19901340
- PMCID: PMC2780806
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0909409106
A t-butyloxycarbonyl-modified Wnt5a-derived hexapeptide functions as a potent antagonist of Wnt5a-dependent melanoma cell invasion
Abstract
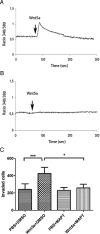
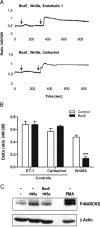
The influential role of Wnt5a in tumor progression underscores the requirement for developing molecules that can target Wnt5a-mediated cellular responses. In the aggressive skin cancer, melanoma, elevated Wnt5a expression promotes cell motility and drives metastasis. Two approaches can be used to counteract these effects: inhibition of Wnt5a expression or direct blockade of Wnt5a signaling. We have investigated both options in the melanoma cell lines, A2058 and HTB63. Both express Frizzled-5, which has been implicated as the receptor for Wnt5a in melanoma cells. However, only the HTB63 cell line expresses and secretes Wnt5a. In these cells, the cytokine, TGFbeta1, controlled the expression of Wnt5a, but due to the unpredictable effects of TGFbeta1 signaling on melanoma cell motility, targeting Wnt5a signaling via TGFbeta1 was an unsuitable strategy to pursue. We therefore attempted to target Wnt5a signaling directly. Exogenous Wnt5a stimulation of A2058 cells increased adhesion, migration and invasion, all crucial components of tumor metastasis, and the Wnt5a-derived N-butyloxycarbonyl hexapeptide (Met-Asp-Gly-Cys-Glu-Leu; 0.766 kDa) termed Box5, abolished these responses. Box5 also inhibited the basal migration and invasion of Wnt5a-expressing HTB63 melanoma cells. Box5 antagonized the effects of Wnt5a on melanoma cell migration and invasion by directly inhibiting Wnt5a-induced protein kinase C and Ca(2+) signaling, the latter of which we directly demonstrate to be essential for cell invasion. The Box5 peptide directly inhibits Wnt5a signaling, representing an approach to anti-metastatic therapy for otherwise rapidly progressive melanoma, and for other Wnt5a-stimulated invasive cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: V.J., V.S., J.H, A.S., L.A., and T.A. have filed a patent on Box5 and its use as an anti-metastatic compound.
Figures


References
-
- Klaus A, Birchmeier W. Wnt signalling and its impact on development and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:387–398. - PubMed
-
- Quaiser T, Anton R, Kühl M. Kinases and G proteins join the Wnt receptor complex. Bioessays. 2006;28:339–343. - PubMed
-
- Slusarski DC, Yang-Snyder J, Busa WB, Moon RT. Modulation of embryonic intracellular Ca2+ signaling by Wnt-5A. Dev Biol. 1997;182:114–120. - PubMed
-
- Säfholm A, Leandersson K, Dejmek J, Nielsen CK, Villoutreix BO, Andersson T. A formylated hexapeptide ligand mimics the ability of Wnt-5a to impair migration of human breast epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:2740–2749. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

