Diet-induced gene expression of isolated pancreatic islets from a polygenic mouse model of the metabolic syndrome
- PMID: 19902174
- PMCID: PMC2797618
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-009-1576-4
Diet-induced gene expression of isolated pancreatic islets from a polygenic mouse model of the metabolic syndrome
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: Numerous new genes have recently been identified in genome-wide association studies for type 2 diabetes. Most are highly expressed in beta cells and presumably play important roles in their function. However, these genes account for only a small proportion of total risk and there are likely to be additional candidate genes not detected by current methodology. We therefore investigated islets from the polygenic New Zealand mouse (NZL) model of diet-induced beta cell dysfunction to identify novel genes and pathways that may play a role in the pathogenesis of diabetes.
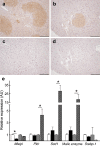
Methods: NZL mice were fed a diabetogenic high-fat diet (HF) or a diabetes-protective carbohydrate-free HF diet (CHF). Pancreatic islets were isolated by laser capture microdissection (LCM) and subjected to genome-wide transcriptome analyses.
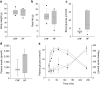
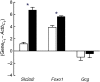
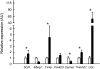
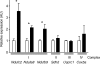
Results: In the prediabetic state, 2,109 islet transcripts were differentially regulated (>1.5-fold) between HF and CHF diets. Of the genes identified, 39 (e.g. Cacna1d, Chd2, Clip2, Igf2bp2, Dach1, Tspan8) correlated with data from the Diabetes Genetics Initiative and Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium genome-wide scans for type 2 diabetes, thus validating our approach. HF diet induced early changes in gene expression associated with increased cell-cycle progression, proliferation and differentiation of islet cells, and oxidative stress (e.g. Cdkn1b, Tmem27, Pax6, Cat, Prdx4 and Txnip). In addition, pathway analysis identified oxidative phosphorylation as the predominant gene-set that was significantly upregulated in response to the diabetogenic HF diet.
Conclusions/interpretation: We demonstrated that LCM of pancreatic islet cells in combination with transcriptional profiling can be successfully used to identify novel candidate genes for diabetes. Our data strongly implicate glucose-induced oxidative stress in disease progression.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

