Preparation and evaluation of thermosensitive liposomal hydrogel for enhanced transcorneal permeation of ofloxacin
- PMID: 19902361
- PMCID: PMC2799601
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-009-9335-x
Preparation and evaluation of thermosensitive liposomal hydrogel for enhanced transcorneal permeation of ofloxacin
Abstract
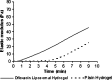
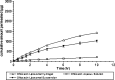
Ofloxacin, available as ophthalmic solution, has two major problems: first, it needs frequent administration every 4 hours or even every 1 hour to treat severe eye infection; second, there is formation of white crystalline deposit on cornea due to its pH-dependent solubility, which is very low at pH of corneal fluid. In order to provide a solution to previous problems, ofloxacin in this study is prepared as topically effective in situ thermosensitive prolonged release liposomal hydrogel. Two preparation procedures were carried out, leading to the formation of multilamellar vesicles (MLVs) and reverse-phase evaporation vesicles (REVs) at pH 7.4. Effects of method of preparation, lipid content, and charge inducers on encapsulation efficiency were studied. For the preparation of in situ thermosensitive hydrogel, chitosan/beta-glycerophosphate system was synthesized and used as carrier for ofloxacin liposomes. The effect of addition of liposomes on gelation temperature, gelation time, and rheological behaviors of the hydrogel were evaluated. In vitro transcorneal permeation was also determined. MLVs entrapped greater amount of ofloxacin than REVs liposomes at pH 7.4; drug loading was increased by including charge-inducing agent and by increasing cholesterol content until a certain limit. The gelation time was decreased by the addition of liposomes into the hydrogel. The prepared liposomal hydrogel enhances the transcorneal permeation sevenfold more than the aqueous solution. These results suggested that the in situ thermosensitive ofloxacin liposomal hydrogel ensures steady and prolonged transcorneal permeation, which improves the ocular bioavailability, minimizes the need for frequent administration, and decreases the ocular side effect of ofloxacin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Optimization of gatifloxacin liposomal hydrogel for enhanced transcorneal permeation.J Liposome Res. 2010 Mar;20(1):31-7. doi: 10.3109/08982100903030255. J Liposome Res. 2010. PMID: 19545203
-
Ciprofloxacin as ocular liposomal hydrogel.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010 Mar;11(1):241-6. doi: 10.1208/s12249-009-9373-4. Epub 2010 Feb 12. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010. PMID: 20151337 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogel Ring for Topical Drug Delivery to the Ocular Posterior Segment.Curr Eye Res. 2016 May;41(5):653-61. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2015.1050738. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Curr Eye Res. 2016. PMID: 26237665
-
Development, Optimization, and In Vitro/In Vivo Characterization of Enhanced Lipid Nanoparticles for Ocular Delivery of Ofloxacin: the Influence of Pegylation and Chitosan Coating.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019 May 3;20(5):183. doi: 10.1208/s12249-019-1371-6. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2019. PMID: 31054011
-
[Transcorneal drug delivery: prospects for the use of liposomes].Vestn Oftalmol. 2014 Jul-Aug;130(4):117-22. Vestn Oftalmol. 2014. PMID: 25306734 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Stress impact of liposomes loaded with ciprofloxacin on the expression level of MepA and NorB efflux pumps of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Int Microbiol. 2022 Aug;25(3):427-446. doi: 10.1007/s10123-021-00219-4. Epub 2021 Nov 25. Int Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 34822035
-
In-vitro and in-vivo evaluation of chitosan-based thermosensitive gel containing lorazepam NLCs for the treatment of status epilepticus.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020 Apr;14(2):148-154. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2019.0156. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32433032 Free PMC article.
-
Donepezil HCl Liposomes: Development, Characterization, Cytotoxicity, and Pharmacokinetic Study.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022 Feb 11;23(2):74. doi: 10.1208/s12249-022-02209-9. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2022. PMID: 35149912
-
Corneal permeability assay of topical eye drop solutions in rabbits by MRI.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2010 Dec;30(6):804-8. doi: 10.1007/s11596-010-0662-7. Epub 2010 Dec 22. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 21181376
-
Liposome-Hydrogel Composites for Controlled Drug Delivery Applications.Gels. 2024 Apr 22;10(4):284. doi: 10.3390/gels10040284. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38667703 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adenis JP, Colin J, Verin P, Saint-Blancat P, Malet F. Ciprofloxacin ophthalmic solution versus rifamycin ophthalmic solution for the treatment of conjunctivitis and blepharitis. Eur J Ophthalmol. 1995;5:82–7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

