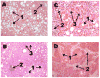
Toxicant-associated steatohepatitis in vinyl chloride workers
- PMID: 19902480
- PMCID: PMC4019991
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.23321
Toxicant-associated steatohepatitis in vinyl chloride workers
Abstract
Although nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is typically associated with obesity, it has also been reported to occur in lean individuals exposed to industrial chemicals. Occupational exposure to vinyl chloride (VC) is a well-documented risk factor for hemangiosarcoma, but has not previously been associated with steatohepatitis. Here we evaluate liver biopsies from 25 nonobese, highly exposed VC workers for steatohepatitis. Next, we evaluate associated metabolic and cytokine abnormalities in affected workers controlled by 26 chemical workers with no to minimal VC exposures, and 11 unexposed, healthy volunteers. Among highly exposed VC workers the prevalence of steatohepatitis was 80%. Of these, 55% had fibrosis and four had hemangiosarcoma. We have coined the term toxicant-associated steatohepatitis (TASH) to describe this condition, which was not explained by obesity or alcohol. Although mean serum transaminases were normal in TASH, total cytokeratin 18, but not the caspase-cleaved fragment, was elevated. Despite the absence of obesity, workers with TASH had insulin resistance with reduced adiponectin levels. TASH was also associated with markedly elevated serum tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukins 1beta, 6, and 8. Serum antioxidant activity was reduced in TASH.
Conclusion: TASH occurred frequently in these nonobese VC workers with high cumulative exposures and normal liver enzymes. Elevated total cytokeratin 18 suggested the presence of necrotic cell death in TASH and may be a useful serologic biomarker. TASH was further characterized by insulin resistance, elevated proinflammatory cytokines, and impaired antioxidant defenses. The threshold VC exposure and the role of other chemical agents in TASH are as yet unknown.
References
-
- Cave M, Deaciuc I, Mendez C, Song Z, Joshi-Barve S, Barve S, McClain C. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: predisposing factors and the role of nutrition. J Nutr Biochem. 2007;18:184–195. - PubMed
-
- Vauthey JN, Pawlik TM, Ribero D, Wu TT, Zorzi D, Hoff PM, Xiong HQ, et al. Chemotherapy regimen predicts steatohepatitis and an increase in 90-day mortality after surgery for hepatic colorectal metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:2065–2072. - PubMed
-
- Cotrim HP, De Freitas LA, Freitas C, Braga L, Sousa R, Carvalho F, Parana R, et al. Clinical and histopathological features of NASH in workers exposed to chemicals with or without associated metabolic conditions. Liver Int. 2004;24:131–135. - PubMed
-
- Day CP, James OF. Steatohepatitis: a tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology. 1998;114:842–845. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical