Targeting phospholipase D with small-molecule inhibitors as a potential therapeutic approach for cancer metastasis
- PMID: 19903073
- PMCID: PMC2814819
- DOI: 10.2217/fon.09.110
Targeting phospholipase D with small-molecule inhibitors as a potential therapeutic approach for cancer metastasis
Abstract
Phospholipase D (PLD)1 and PLD2, the classic mammalian members of the PLD superfamily, have been linked over the past three decades to immune cell function and to cell biological processes required by cancer cells for metastasis. However, owing to the lack of effective small-molecule inhibitors, it has not been possible to validate these roles for the PLDs and to explore the possible utility of acute and chronic PLD inhibition in vivo. The first such inhibitors have recently been described and demonstrated to block neutrophil chemotaxis and invasion by breast cancer cells in culture, increasing the prospects for a new class of therapeutics for autoimmune disorders and several types of metastatic cancer.
Figures
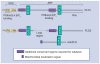
References
-
- Mcdermott M, Wakelam MJ, Morris AJ. Phospholipase D. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004;82(1):225–253. - PubMed
-
- Mor A, Campi G, Du G, et al. The lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 receptor costimulates plasma membrane ras via phospholipase D2. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007;9:712–719. - PubMed
-
-
Zhao C, Du G, Skowronek K, Frohman MA, Bar-Sagi D. Phospholipase D2-generated phosphatidic acid couples EGFR stimulation to ras activation by sos. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007;9:707–712.▪ Landmark paper linking phospholipase D2 (PLD2) to direct activation of Ras, a key signaling player in many types of cancer.
-
-
- Delon C, Manifava M, Wood E, et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 is an intracellular effector of phosphatidic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279(43):44763–44774. - PubMed
-
- Ha SH, Kim DH, Kim IS, et al. PLD2 forms a functional complex with MTOR/Raptor to transduce mitogenic signals. Cell. Signal. 2006;18(12):2283–2291. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
