Pediatric influenza-associated myositis - Nebraska, 2001-2007
- PMID: 19903210
- PMCID: PMC4941392
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-2659.2009.00102.x
Pediatric influenza-associated myositis - Nebraska, 2001-2007
Abstract
Objective: Influenza-associated myositis (IAM), characterized by severe lower-extremity myalgia and reluctance to walk, is a complication of influenza among children. We investigated IAM in Nebraska during six influenza seasons, 2001-2007.
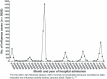
Methods: During 2006-2007, we requested reports of severe influenza illness among persons aged <18 years and investigated medical records to identify and confirm IAM cases defined as severe myalgia with elevated serum creatinine kinase level in a patient aged <18 years, occurring within 7 days of laboratory confirmed influenza illness onset. Statewide hospital discharge data (HDD) were reviewed to identify retrospectively confirmed IAM cases during 2006-2007 and five previous seasons, by using surveillance data to define periods of influenza activity. Statewide IAM incidence was estimated for 2001-2002 through 2006-2007.
Results: During 2006-2007, a total of 13 IAM cases were confirmed by enhanced surveillance. Median age was 6 years (range, 4-11 years). Influenza diagnosis was established by viral isolation from six patients (one influenza A and five influenza B) and rapid diagnostic tests for seven. Twelve (92%) patients, including one who died, were hospitalized for a median of 3 days (range, 1-4 days). Review of HDD identified 12 retrospectively confirmed IAM cases during 2006-2007, including four not reported through enhanced surveillance, and only one during five previous seasons (2003-2004). The HDD-derived, retrospectively confirmed statewide IAM incidence estimates/100,000 population aged <18 years were 2.693 and 0.225 during 2006-2007 and 2003-2004, respectively.
Conclusion: An IAM epidemic occurred in Nebraska during the 2006-2007 influenza season.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influenza-associated myositis: a single-centre, 5-year retrospective study.Eur J Pediatr. 2021 Feb;180(2):577-584. doi: 10.1007/s00431-020-03835-w. Epub 2020 Oct 23. Eur J Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33095429
-
Influenza-associated myositis in children.Infection. 2004 Aug;32(4):199-203. doi: 10.1007/s15010-004-4003-2. Infection. 2004. PMID: 15293074 Review.
-
[Myosotis in children with flu; a rare complication of influenza].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2017;161:D1265. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2017. PMID: 28832293 Review. Dutch.
-
A large outbreak of influenza B-associated benign acute childhood myositis in Germany, 2007/2008.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011 Aug;30(8):e142-6. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e318217e356. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2011. PMID: 21753259
-
Benign Acute Childhood Myositis During Influenza B Outbreak.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1039:29-34. doi: 10.1007/5584_2017_79. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 28795360
Cited by
-
Acute Kidney Injury Among Children Admitted With Viral Rhabdomyolysis.Hosp Pediatr. 2021 Aug;11(8):878-885. doi: 10.1542/hpeds.2020-005108. Hosp Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34301717 Free PMC article.
-
The burden of seasonal and pandemic influenza in infants and children.Eur J Pediatr. 2014 Mar;173(3):265-76. doi: 10.1007/s00431-013-2023-6. Epub 2013 May 10. Eur J Pediatr. 2014. PMID: 23661234 Free PMC article.
-
A rare presentation of benign acute childhood myositis.Clin Case Rep. 2019 Jan 29;7(3):461-464. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.2001. eCollection 2019 Mar. Clin Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 30899472 Free PMC article.
-
BiologicalNetworks--tools enabling the integration of multi-scale data for the host-pathogen studies.BMC Syst Biol. 2011 Jan 14;5:7. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-5-7. BMC Syst Biol. 2011. PMID: 21235794 Free PMC article.
-
Viral Myositis Secondary to Influenza A in a Preschool Child in Saudi Arabia: A Case Report.Cureus. 2024 Jan 29;16(1):e53179. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53179. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38420103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Neuzil KM, Mellen BG, Wright PF, Mitchel EF Jr, Griffin MR. The effect of influenza on hospitalizations, outpatient visits, and courses of antibiotics in children. N Engl J Med 2000; 342:225–231. - PubMed
-
- Peltola V, Zieglar T, Ruuskanen O. Influenza A and B virus infections in children. Clin Infect Dis 2003; 36:299–305. - PubMed
-
- Thompson WW, Shay DK, Weintraub E et al. Influenza‐associated hospitalizations in the United States. JAMA 2004; 292:1333–1340. - PubMed
-
- Izurieta HS, Thompson WW, Kramarz P et al. Influenza and the rates of hospitalization for respiratory disease among infants and young children. N Engl J Med 2000; 342:232–239. - PubMed
-
- Agyeman P, Duppenthaler A, Heininger U, Aebi C. Influenza‐associated myositis in children. Infection 2004; 32:199–203. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical