Neuroticism as a common dimension in the internalizing disorders
- PMID: 19903363
- PMCID: PMC2882529
- DOI: 10.1017/S0033291709991449
Neuroticism as a common dimension in the internalizing disorders
Abstract
Background: Several theories have posited a common internalizing factor to help account for the relationship between mood and anxiety disorders. These disorders are often co-morbid and strongly covary. Other theories and data suggest that personality traits may account, at least in part, for co-morbidity between depression and anxiety. The present study examined the relationship between neuroticism and an internalizing dimension common to mood and anxiety disorders.
Method: A sample of ethnically diverse adolescents (n=621) completed self-report and peer-report measures of neuroticism. Participants also completed the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV (SCID).
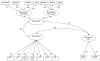
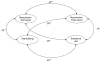
Results: Structural equation modeling showed that a single internalizing factor was common to lifetime diagnosis of mood and anxiety disorders, and this internalizing factor was strongly correlated with neuroticism. Neuroticism had a stronger correlation with an internalizing factor (r=0.98) than with a substance use factor (r=0.29). Therefore, neuroticism showed both convergent and discriminant validity.
Conclusions: These results provide further evidence that neuroticism is a necessary factor in structural theories of mood and anxiety disorders. In this study, the correlation between internalizing psychopathology and neuroticism approached 1.0, suggesting that neuroticism may be the core of internalizing psychopathology. Future studies are needed to examine this possibility in other populations, and to replicate our findings.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The anxiety disorders and suicidal ideation: accounting for co-morbidity via underlying personality traits.Psychol Med. 2011 Jul;41(7):1437-47. doi: 10.1017/S0033291710002096. Epub 2010 Nov 8. Psychol Med. 2011. PMID: 21054917
-
Is the generalized anxiety disorder symptom of worry just another form of neuroticism? a 5-year longitudinal study of adolescents from the general population.J Clin Psychiatry. 2010 Jul;71(7):942-8. doi: 10.4088/JCP.09m05506blu. Epub 2010 May 4. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20492844
-
The Northwestern-UCLA youth emotion project: Associations of cognitive vulnerabilities, neuroticism and gender with past diagnoses of emotional disorders in adolescents.Behav Res Ther. 2010 May;48(5):347-58. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2009.12.008. Epub 2009 Dec 23. Behav Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20070951 Free PMC article.
-
Association of eating disorder symptoms with internalizing and externalizing dimensions of psychopathology among men and women.Int J Eat Disord. 2014 Dec;47(8):860-9. doi: 10.1002/eat.22300. Epub 2014 May 22. Int J Eat Disord. 2014. PMID: 24849585 Free PMC article.
-
Factor structure of self-reported clinical disorders and personality disorders: a review of the existing literature and a factor analytical study.J Clin Psychol. 2012 Jun;68(6):645-60. doi: 10.1002/jclp.21841. Epub 2012 Mar 30. J Clin Psychol. 2012. PMID: 22467345 Review.
Cited by
-
Leveraging digital technology to intervene on personality processes to promote healthy aging.Personal Disord. 2019 Jan;10(1):33-45. doi: 10.1037/per0000275. Personal Disord. 2019. PMID: 30604982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of traits and functional connectivity-based neurotraits of chronic pain.PLoS Biol. 2019 Aug 20;17(8):e3000349. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000349. eCollection 2019 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2019. PMID: 31430270 Free PMC article.
-
Personality, depression and anxiety in primary Sjogren's syndrome - Association with sociodemographic factors and comorbidity.PLoS One. 2019 Jan 17;14(1):e0210466. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210466. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30653543 Free PMC article.
-
Connecting quantitatively derived personality-psychopathology models and neuroscience.Personal Neurosci. 2021 Oct 8;4:e4. doi: 10.1017/pen.2021.3. eCollection 2021. Personal Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34909563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comorbidity of anxiety and depression in children and adolescents: 20 years after.Psychol Bull. 2014 May;140(3):816-45. doi: 10.1037/a0034733. Epub 2013 Nov 11. Psychol Bull. 2014. PMID: 24219155 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Achenbach TM, Krukowski RA, Dumenci L, Ivanova MY. Assessment of adult psychopathology: Meta-analyses and implications of cross-informant correlations. Psychological Bulletin. 2005;131:361–382. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th text revision ed Author; Washington, DC: 2000.
-
- Bagby RM, Parker JDA. Relation of rumination and distraction with neuroticism and extraversion in a sample of patients with major depression. Cognitive Therapy and Research. 2001;25:91–102.
-
- Bentler PM. Comparative fix indexes in structural models. Psychological Bulletin. 1988;107:238–246. - PubMed
-
- Brown TA, Barlow DH. Classification of mood and anxiety disorders. In: Barlow DH, editor. Anxiety and Its Disorders: The Nature and Treatment of Anxiety and Panic. 2nd ed The Guilford Press; New York: 2002.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

