Chapter 11 - Reconstitution of membrane proteins in phospholipid bilayer nanodiscs
- PMID: 19903557
- PMCID: PMC4196316
- DOI: 10.1016/S0076-6879(09)64011-8
Chapter 11 - Reconstitution of membrane proteins in phospholipid bilayer nanodiscs
Abstract
Self-assembled phospholipid bilayer Nanodiscs have become an important and versatile tool among model membrane systems to functionally reconstitute membrane proteins. Nanodiscs consist of lipid domains encased within an engineered derivative of apolipoprotein A-1 scaffold proteins, which can be tailored to yield homogeneous preparations of disks with different diameters, and with epitope tags for exploitation in various purification strategies. A critical aspect of the self-assembly of target membranes into Nanodiscs lies in the optimization of the lipid:protein ratio. Here we describe strategies for performing this optimization and provide examples for reconstituting bacteriorhodopsin as a trimer, rhodopsin, and functionally active P-glycoprotein. Together, these demonstrate the versatility of Nanodisc technology for preparing monodisperse samples of membrane proteins of wide-ranging structure.
Figures

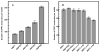

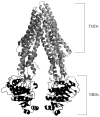
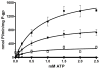
References
-
- Adachi Y, Suzuki H, Sugiyama Y. Comparative studies on in vitro methods for evaluating in vivo function of MDR1 P-glycoprotein. Pharm Res. 2001;18:1660–8. - PubMed
-
- Ambudkar SV, Lelong IH, Zhang J, Cardarelli C. Purification and reconstitution of human P-glycoprotein. Methods Enzymol. 1998;292:492–504. - PubMed
-
- Baas BJ, Denisov IG, Sligar SG. Homotropic cooperativity of monomeric cytochrome P450 3A4 in a nanoscale native bilayer environment. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2004;430:218–228. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

