Regulation of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels (Cav2.2) and transmitter release by collapsin response mediator protein-2 (CRMP-2) in sensory neurons
- PMID: 19903690
- PMCID: PMC2779133
- DOI: 10.1242/jcs.053280
Regulation of N-type voltage-gated calcium channels (Cav2.2) and transmitter release by collapsin response mediator protein-2 (CRMP-2) in sensory neurons
Abstract
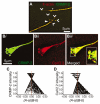
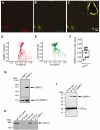
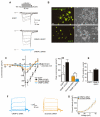
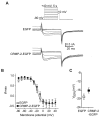
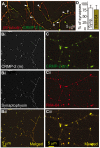
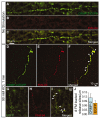
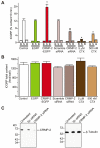
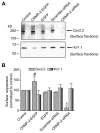
Collapsin response mediator proteins (CRMPs) mediate signal transduction of neurite outgrowth and axonal guidance during neuronal development. Voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels and interacting proteins are essential in neuronal signaling and synaptic transmission during this period. We recently identified the presynaptic N-type voltage-gated Ca(2+) channel (Cav2.2) as a CRMP-2-interacting partner. Here, we investigated the effects of a functional association of CRMP-2 with Cav2.2 in sensory neurons. Cav2.2 colocalized with CRMP-2 at immature synapses and growth cones, in mature synapses and in cell bodies of dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons. Co-immunoprecipitation experiments showed that CRMP-2 associates with Cav2.2 from DRG lysates. Overexpression of CRMP-2 fused to enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) in DRG neurons, via nucleofection, resulted in a significant increase in Cav2.2 current density compared with cells expressing EGFP. CRMP-2 manipulation changed the surface levels of Cav2.2. Because CRMP-2 is localized to synaptophysin-positive puncta in dense DRG cultures, we tested whether this CRMP-2-mediated alteration of Ca(2+) currents culminated in changes in synaptic transmission. Following a brief high-K(+)-induced stimulation, these puncta became loaded with FM4-64 dye. In EGFP and neurons expressing CRMP-2-EGFP, similar densities of FM-loaded puncta were observed. Finally, CRMP-2 overexpression in DRG increased release of the immunoreactive neurotransmitter calcitonin gene-related peptide (iCGRP) by approximately 70%, whereas siRNA targeting CRMP-2 significantly reduced release of iCGRP by approximately 54% compared with control cultures. These findings support a novel role for CRMP-2 in the regulation of N-type Ca(2+) channels and in transmitter release.
Figures

Similar articles
-
An atypical role for collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP-2) in neurotransmitter release via interaction with presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 6;284(45):31375-90. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.009951. Epub 2009 Sep 15. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19755421 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of collapsin response mediator proteins (CRMPs) as regulators of voltage-gated calcium channels and synaptic transmission.Commun Integr Biol. 2010 Mar;3(2):172-5. doi: 10.4161/cib.3.2.10620. Commun Integr Biol. 2010. PMID: 20585514 Free PMC article.
-
AAV-encoded CaV2.2 peptide aptamer CBD3A6K for primary sensory neuron-targeted treatment of established neuropathic pain.Gene Ther. 2019 Aug;26(7-8):308-323. doi: 10.1038/s41434-019-0082-7. Epub 2019 May 22. Gene Ther. 2019. PMID: 31118475 Free PMC article.
-
Challenging the catechism of therapeutics for chronic neuropathic pain: Targeting CaV2.2 interactions with CRMP2 peptides.Neurosci Lett. 2013 Dec 17;557 Pt A(0 0):27-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.06.057. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Neurosci Lett. 2013. PMID: 23831344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presynaptic calcium channels.Neurosci Res. 2018 Feb;127:33-44. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2017.09.012. Epub 2018 Jan 6. Neurosci Res. 2018. PMID: 29317246 Review.
Cited by
-
Neurologic orphan diseases: Emerging innovations and role for genetic treatments.World J Exp Med. 2023 Sep 20;13(4):59-74. doi: 10.5493/wjem.v13.i4.59. eCollection 2023 Sep 20. World J Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 37767543 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Regulation of DNA Methylation at the CRMP2 Promoter Region Between the Hippocampus and Prefrontal Cortex in a CUMS Depression Model.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Mar 18;11:141. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00141. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32256396 Free PMC article.
-
Cdk5-mediated CRMP2 phosphorylation is necessary and sufficient for peripheral neuropathic pain.Neurobiol Pain. 2019 Jan-Jul;5:100022. doi: 10.1016/j.ynpai.2018.07.003. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Neurobiol Pain. 2019. PMID: 31080913 Free PMC article.
-
Further insights into the antinociceptive potential of a peptide disrupting the N-type calcium channel-CRMP-2 signaling complex.Channels (Austin). 2011 Sep-Oct;5(5):449-56. doi: 10.4161/chan.5.5.17363. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Channels (Austin). 2011. PMID: 21829088 Free PMC article.
-
Post-translational modifications of voltage-gated sodium channels in chronic pain syndromes.Front Pharmacol. 2015 Nov 5;6:263. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00263. eCollection 2015. Front Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26594175 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alvarez, F. J., Kavookjian, A. M. and Light, A. R. (1993). Ultrastructural morphology, synaptic relationships, and CGRP immunoreactivity of physiologically identified C-fiber terminals in the monkey spinal cord. J. Comp Neurol. 329, 472-490. - PubMed
-
- Ambalavanar, R., Moritani, M., Moutanni, A., Gangula, P., Yallampalli, C. and Dessem, D. (2006). Deep tissue inflammation upregulates neuropeptides and evokes nociceptive behaviors which are modulated by a neuropeptide antagonist. Pain 120, 53-68. - PubMed
-
- Augustine, G. J. (2001). How does calcium trigger neurotransmitter release? Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 11, 320-326. - PubMed
-
- Bahls, F. H., Lartius, R., Trudeau, L. E., Doyle, R. T., Fang, Y., Witcher, D., Campbell, K. and Haydon, P. G. (1998). Contact-dependent regulation of N-type calcium channel subunits during synaptogenesis. J. Neurobiol. 35, 198-208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

