Kidins220/ARMS modulates the activity of microtubule-regulating proteins and controls neuronal polarity and development
- PMID: 19903810
- PMCID: PMC2801261
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.024703
Kidins220/ARMS modulates the activity of microtubule-regulating proteins and controls neuronal polarity and development
Abstract
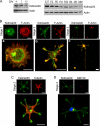
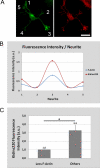
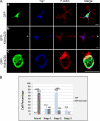
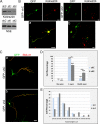
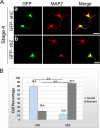
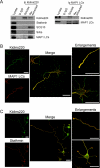
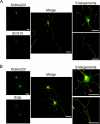
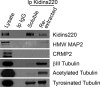
In order for neurons to perform their function, they must establish a highly polarized morphology characterized, in most of the cases, by a single axon and multiple dendrites. Herein we find that the evolutionarily conserved protein Kidins220 (kinase D-interacting substrate of 220-kDa), also known as ARMS (ankyrin repeat-rich membrane spanning), a downstream effector of protein kinase D and neurotrophin and ephrin receptors, regulates the establishment of neuronal polarity and development of dendrites. Kidins220/ARMS gain and loss of function experiments render severe phenotypic changes in the processes extended by hippocampal neurons in culture. Although Kidins220/ARMS early overexpression hinders neuronal development, its down-regulation by RNA interference results in the appearance of multiple longer axon-like extensions as well as aberrant dendritic arbors. We also find that Kidins220/ARMS interacts with tubulin and microtubule-regulating molecules whose role in neuronal morphogenesis is well established (microtubule-associated proteins 1b, 1a, and 2 and two members of the stathmin family). Importantly, neurons where Kidins220/ARMS has been knocked down register changes in the phosphorylation activity of MAP1b and stathmins. Altogether, our results indicate that Kidins220/ARMS is a key modulator of the activity of microtubule-regulating proteins known to actively regulate neuronal morphogenesis and suggest a mechanism by which it contributes to control neuronal development.
Figures

References
-
- Arimura N., Kaibuchi K. (2007) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 8, 194–205 - PubMed
-
- da Silva J. S., Dotti C. G. (2002) Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 694–704 - PubMed
-
- Da Silva J. S., Hasegawa T., Miyagi T., Dotti C. G., Abad-Rodriguez J. (2005) Nat. Neurosci. 8, 606–615 - PubMed
-
- Horton A. C., Ehlers M. D. (2003) Neuron 40, 277–295 - PubMed
-
- Bradke F., Dotti C. G. (2000) Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 10, 574–581 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

