NFkappaB p50-CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta)-mediated transcriptional repression of microRNA let-7i following microbial infection
- PMID: 19903813
- PMCID: PMC2804168
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.041640
NFkappaB p50-CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta)-mediated transcriptional repression of microRNA let-7i following microbial infection
Abstract
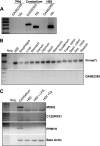
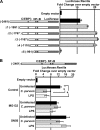
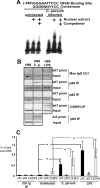
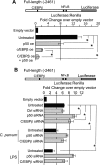
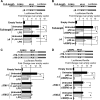
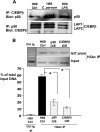
MicroRNAs, central players of numerous cellular processes, regulate mRNA stability or translational efficiency. Although these molecular events are established, the mechanisms regulating microRNA function and expression remain largely unknown. The microRNA let-7i regulates Toll-like receptor 4 expression. Here, we identify a novel transcriptional mechanism induced by the protozoan parasite Cryptosporidium parvum and Gram(-) bacteria-derived lipopolysaccharide (LPS) mediating let-7i promoter silencing in human biliary epithelial cells (cholangiocytes). Using cultured cholangiocytes, we show that microbial stimulus decreased let-7i expression, and promoter activity. Analysis of the mechanism revealed that microbial infection promotes the formation of a NFkappaB p50-C/EBPbeta silencer complex in the regulatory sequence. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays (ChIP) demonstrated that the repressor complex binds to the let-7i promoter following microbial stimulus and promotes histone-H3 deacetylation. Our results provide a novel mechanism of transcriptional regulation of cholangiocyte let-7i expression following microbial insult, a process with potential implications for epithelial innate immune responses in general.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A cellular micro-RNA, let-7i, regulates Toll-like receptor 4 expression and contributes to cholangiocyte immune responses against Cryptosporidium parvum infection.J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 28;282(39):28929-28938. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M702633200. Epub 2007 Jul 27. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17660297 Free PMC article.
-
Cryptosporidium parvum induces SIRT1 expression in host epithelial cells through downregulating let-7i.Hum Immunol. 2014 Aug;75(8):760-5. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2014.05.007. Epub 2014 May 24. Hum Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24862934 Free PMC article.
-
Histone deacetylases and NF-kB signaling coordinate expression of CX3CL1 in epithelial cells in response to microbial challenge by suppressing miR-424 and miR-503.PLoS One. 2013 May 28;8(5):e65153. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0065153. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23724129 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of the MIR155 host gene in physiological and pathological processes.Gene. 2013 Dec 10;532(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2012.12.009. Epub 2012 Dec 14. Gene. 2013. PMID: 23246696 Review.
-
Dual mechanism of Let-7i in tumor progression.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 27;13:1253191. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1253191. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37829341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Boswellic acid exerts antitumor effects in colorectal cancer cells by modulating expression of the let-7 and miR-200 microRNA family.Carcinogenesis. 2012 Dec;33(12):2441-9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgs286. Epub 2012 Sep 15. Carcinogenesis. 2012. PMID: 22983985 Free PMC article.
-
A Systematic Review of Apicomplexa Looking into Epigenetic Pathways and the Opportunity for Novel Therapies.Pathogens. 2023 Feb 11;12(2):299. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12020299. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 36839571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-29 modulates Wnt signaling in human osteoblasts through a positive feedback loop.J Biol Chem. 2010 Aug 13;285(33):25221-31. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.116137. Epub 2010 Jun 15. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20551325 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Infection-Induced Suppression of the Let-7i/IL-2 Axis Contributes to CD4(+) T Cell Death.Sci Rep. 2016 May 5;6:25341. doi: 10.1038/srep25341. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27145859 Free PMC article.
-
microRNAs in parasites and parasite infection.RNA Biol. 2013 Mar;10(3):371-9. doi: 10.4161/rna.23716. Epub 2013 Feb 7. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 23392243 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harada K., Ohba K., Ozaki S., Isse K., Hirayama T., Wada A., Nakanuma Y. (2004) Hepatology 40, 925–932 - PubMed
-
- Yokoyama T., Komori A., Nakamura M., Takii Y., Kamihira T., Shimoda S., Mori T., Fujiwara S., Koyabu M., Taniguchi K., Fujioka H., Migita K., Yatsuhashi H., Ishibashi H. (2006) Liver Int. 26, 467–476 - PubMed
-
- Chen X. M., Levine S. A., Splinter P. L., Tietz P. S., Ganong A. L., Jobin C., Gores G. J., Paya C. V., LaRusso N. F. (2001) Gastroenterology 120, 1774–1783 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

