Identification of TNF-alpha and MMP-9 as potential baseline predictive serum markers of sunitinib activity in patients with renal cell carcinoma using a human cytokine array
- PMID: 19904265
- PMCID: PMC2788252
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605409
Identification of TNF-alpha and MMP-9 as potential baseline predictive serum markers of sunitinib activity in patients with renal cell carcinoma using a human cytokine array
Abstract
Background: Several drugs are available to treat metastatic renal-cell carcinoma (MRCC), and predictive markers to identify the most adequate treatment for each patient are needed. Our objective was to identify potential predictive markers of sunitinib activity in MRCC.
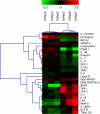
Methods: We collected sequential serum samples from 31 patients treated with sunitinib. Sera of six patients with extreme phenotypes of either marked responses or clear progressions were analysed with a Human Cytokine Array which evaluates 174 cytokines before and after treatment. Variations in cytokine signal intensity were compared between both groups and the most relevant cytokines were assessed by ELISA in all the patients.
Results: Twenty-seven of the 174 cytokines varied significantly between both groups. Five of them (TNF-alpha, MMP-9, ICAM-1, BDNF and SDF-1) were assessed by ELISA in 21 evaluable patients. TNF-alpha and MMP-9 baseline levels were significantly increased in non-responders and significantly associated with reduced overall survival and time-to-progression, respectively. The area under the ROC curves for TNF-alpha and MMP-9 as predictive markers of sunitinib activity were 0.83 and 0.77.
Conclusion: Baseline levels of TNF-alpha and MMP-9 warrant further study as predictive markers of sunitinib activity in MRCC. Selection of patients with extreme phenotypes seems a valid method to identify potential predictive factors of response.
Figures



References
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Ser B 57: 289–300
-
- Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (2000) On the adaptive control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing with independent statistics. J Edu Behav Stat 25: 60–83
-
- Choueiri TK, Garcia JA, Elson P, Khasawneh M, Usman S, Golshayan AR, Baz RC, Wood L, Rini BI, Bukowski RM (2007) Clinical factors associated with outcome in patients with metastatic clear-cell renal cell carcinoma treated with vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapy. Cancer 110: 543–550 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

