Mindfulness training and stress reactivity in substance abuse: results from a randomized, controlled stage I pilot study
- PMID: 19904666
- PMCID: PMC3045038
- DOI: 10.1080/08897070903250241
Mindfulness training and stress reactivity in substance abuse: results from a randomized, controlled stage I pilot study
Abstract
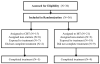
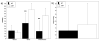
Stress is important in substance use disorders (SUDs). Mindfulness training (MT) has shown promise for stress-related maladies. No studies have compared MT to empirically validated treatments for SUDs. The goals of this study were to assess MT compared to cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) in substance use and treatment acceptability, and specificity of MT compared to CBT in targeting stress reactivity. Thirty-six individuals with alcohol and/or cocaine use disorders were randomly assigned to receive group MT or CBT in an outpatient setting. Drug use was assessed weekly. After treatment, responses to personalized stress provocation were measured. Fourteen individuals completed treatment. There were no differences in treatment satisfaction or drug use between groups. The laboratory paradigm suggested reduced psychological and physiological indices of stress during provocation in MT compared to CBT. This pilot study provides evidence of the feasibility of MT in treating SUDs and suggests that MT may be efficacious in targeting stress.
Figures

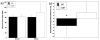
References
-
- Sinha R, Talih M, Malison R, Cooney N, Anderson GM, Kreek MJ. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and sympatho-adreno-medullary responses during stress-induced and drug cue-induced cocaine craving states. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2003;170(1):62–72. - PubMed
-
- Cabib S, Puglisi-Allegra S, Genua C, Simon H, Le Moal M, Piazza PV. Dose-dependent aversive and rewarding effects of amphetamine as revealed by a new place conditioning apparatus. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1996;125(1):92–6. - PubMed
-
- Kalivas PW, Duffy P. Similar effects of daily cocaine and stress on mesocorticolimbic dopamine neurotransmission in the rat. Biol Psychiatry. 1989;25(7):913–28. - PubMed
-
- Volpicelli JR. Uncontrollable events and alcohol drinking. Br J Addict. 1987;82(4):381–92. - PubMed
-
- O'Brien CP, Childress AR, Ehrman R, Robbins SJ. Conditioning factors in drug abuse: can they explain compulsion? J Psychopharmacol. 1998;12(1):15–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- T32-DA007238/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K12-DA00167/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- RL1 AA017539/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- K05-DA00457/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA009241/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50-DA16556/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA000457/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K12 DA000167/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA020908/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37-DA15969/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA016556/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA019039/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA017232/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA000089/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DA015969/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02-DA17232/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007238/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05-DA00089/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50-DA09241/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

