Independent roles of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and endogenous, but not exogenous glucocorticoids in regulating leukocyte trafficking
- PMID: 19905972
- PMCID: PMC3070174
- DOI: 10.3109/10739680903210421
Independent roles of macrophage migration inhibitory factor and endogenous, but not exogenous glucocorticoids in regulating leukocyte trafficking
Abstract
Objectives: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) promotes leukocyte recruitment and antagonizes the anti-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids (GC). The aim of this study was to examine whether interaction between MIF and GC underlies the ability of MIF to promote leukocyte-endothelial cell (EC) interactions.
Methods: Intravital microscopy was used to assess leukocyte-EC interactions in wild-type and MIF(-/-) mice following treatment with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), the GC dexamethasone, and inhibition of endogenous GC, using the GC-receptor antagonist, RU486.
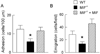
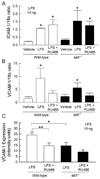
Results: Dexamethasone reduced LPS-induced leukocyte interactions in wild-type mice to levels similar to those observed in MIF(-/-) mice not treated with dexamethasone, whereas in MIF(-/-) mice, leukocyte interactions were not further inhibited by dexamethasone. RU486 increased LPS-induced leukocyte adhesion and emigration to a similar extent in both wild-type and MIF(-/-) mice, indicating that endogenous GC exert a similar inhibitory effect on leukocyte trafficking in wild-type and MIF(-/-) mice. Both MIF deficiency and RU486 treatment reduced VCAM-1 expression, while neither treatment modulated expression of ICAM-1 or chemokines CCL2, KC, and MIP-2.
Conclusions: These results suggest that endogenous MIF and GC regulate leukocyte-EC interactions in vivo reciprocally but through predominantly independent mechanisms, and that the anti-inflammatory effect of MIF deficiency is comparable to that of exogenous GC.
Figures



References
-
- Aeberli D, Yang YH, Mansell A, Santos L, Leech M, Morand EF. Endogenous macrophage migration inhibitory factor modulates glucocorticoid sensitivity in macrophages via effects on MAP kinase phosphatase-1 and p38 MAP kinase. FEBS Lett. 2006;580:974–981. - PubMed
-
- Bernhagen J, Calandra T, Mitchell RA, Martin SB, Tracey KJ, Voelter W, Manogue KR, Cerami A, Bucala R. MIF is a pituitary-derived cytokine that potentiates lethal endotoxaemia. Nature. 1993;365:756–759. - PubMed
-
- Bernhagen J, Krohn R, Lue H, Gregory JL, Zernecke A, Koenen RR, Dewor M, Georgiev I, Schober A, Leng L, Kooistra T, Fingerle-Rowson G, Ghezzi P, Kleemann R, McColl SR, Bucala R, Hickey MJ, Weber C. MIF is a noncognate ligand of CXC chemokine receptors in inflammatory and atherogenic cell recruitment. Nat Med. 2007;13:587–596. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

