The National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) Collaboration for Leadership in Applied Health Research and Care (CLAHRC) for Leicestershire, Northamptonshire and Rutland (LNR): a programme protocol
- PMID: 19906317
- PMCID: PMC2780974
- DOI: 10.1186/1748-5908-4-72
The National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) Collaboration for Leadership in Applied Health Research and Care (CLAHRC) for Leicestershire, Northamptonshire and Rutland (LNR): a programme protocol
Abstract
Background: In October 2008, the National Institute for Health Research launched nine new research projects to develop and investigate methods of translating research evidence into practice. Given the title Collaborations for Leadership in Applied Health Research and Care (CLAHRC), all involve collaboration between one or more universities and the local health service, but they are adopting different approaches to achieve translation.
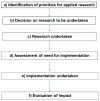
Methods: The translation and implementation programme of this CLAHRC has been built around a pragmatic framework for undertaking research to address live concerns in the delivery of care, in partnership with the managers, practitioners, and patients of the provider organisations of the CLAHRC. Focused on long-term conditions, the constituent research themes are prevention, early detection, self-management, rehabilitation, and implementation. Individual studies have various designs, and include both randomised trials of new ways to deliver care and qualitative studies of, for example, means of identifying barriers to research translation. A mix of methods will be used to evaluate the CLAHRC as a whole, including use of public health indicators, social research methods, and health economics.
Discussion: This paper describes one of the nine collaborations, that of Leicestershire, Northamptonshire, and Rutland. Drawing a distinction between translation as an organising principle for healthcare providers and implementation as a discrete activity, this collaboration is built on a substantial programme of applied research intended to create both research generation and research use capacity in provider organisations. The collaboration in Leicestershire, Northamptonshire, and Rutland has potential to provide evidence on how partnerships between practitioners, patients, and researchers can improve the transfer of evidence into practice.
Figures
References
-
- National Institute for Health Research. Collaborations for Leadership in Applied research and Care. Call for proposals. http://www.nihr.ac.uk/infrastructure/Pages/infrastructure_clahrcs.aspx (accessed 190609).
-
- Cooksey D. A review of UK health research funding. London: The Stationery Office; 2006.
-
- Health Economics Research Group, Office of Health Economics, RAND Europe. Medical research: what's it worth? Estimating the economic benefits from medical research in the UK. London: UK Evaluation Forum; 2008.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources