Resolvin E1 receptor activation signals phosphorylation and phagocytosis
- PMID: 19906641
- PMCID: PMC2823415
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.044131
Resolvin E1 receptor activation signals phosphorylation and phagocytosis
Abstract
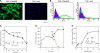
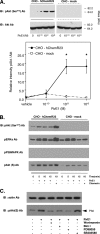
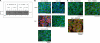
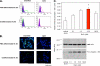
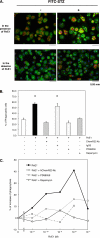
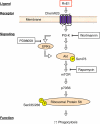
Resolvins are endogenous lipid mediators that actively regulate the resolution of acute inflammation. Resolvin E1 (RvE1; (5S,12R,18R)-trihydroxy-6Z,8E,10E,14Z,16E-eicosapentaenoic acid) is an endogenous anti-inflammatory and pro-resolving mediator derived from eicosapentaenoic acid that regulates leukocyte migration and enhances macrophage phagocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils to resolve inflammation. In the inflammatory milieu, RvE1 mediates counter-regulatory actions initiated via specific G protein-coupled receptors. Here, we have identified RvE1-specific signaling pathways initiated by the RvE1 receptor ChemR23. RvE1 stimulated phosphorylation of Akt that was both ligand- and receptor-dependent. RvE1 regulated Akt phosphorylation in a time (0-15 min)- and dose-dependent (0.01-100 nm) manner in human ChemR23-transfected Chinese hamster ovary cells. RvE1 stimulated phosphorylation of both Akt and a 30-kDa protein, a downstream target of Akt, identified using a phospho-Akt substrate antibody. The 30-kDa protein was identified as ribosomal protein S6, a translational regulator, and its phosphorylation was inhibited by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor (wortmannin) and an ERK inhibitor (PD98059) but not by a p38-MAPK inhibitor (SB203580). Ribosomal protein S6 is a downstream target of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway as well as the Raf/ERK pathway. In ChemR23-expressing differentiated HL60 cells, RvE1 also stimulated the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. In addition, RvE1 enhanced phagocytosis of zymosan A by human macrophages, which are inhibited by PD98059 and rapamycin (mTOR inhibitor). These results indicate that RvE1 initiates direct activation of ChemR23 and signals receptor-dependent phosphorylation. These phosphorylation-signaling pathways identified for RvE1 receptor-ligand interactions underscore the importance of endogenous pro-resolving agonists in resolving acute inflammation.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

