RAGE-dependent signaling in microglia contributes to neuroinflammation, Abeta accumulation, and impaired learning/memory in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 19906677
- PMCID: PMC3231946
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.09-139634
RAGE-dependent signaling in microglia contributes to neuroinflammation, Abeta accumulation, and impaired learning/memory in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
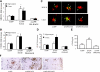
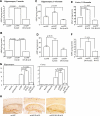
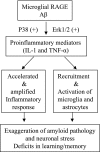
Microglia are critical for amyloid-beta peptide (Abeta)-mediated neuronal perturbation relevant to Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis. We demonstrate that overexpression of receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) in imbroglio exaggerates neuroinflammation, as evidenced by increased proinflammatory mediator production, Abeta accumulation, impaired learning/memory, and neurotoxicity in an Abeta-rich environment. Transgenic (Tg) mice expressing human mutant APP (mAPP) in neurons and RAGE in microglia displayed enhanced IL-1beta and TNF-alpha production, increased infiltration of microglia and astrocytes, accumulation of Abeta, reduced acetylcholine esterase (AChE) activity, and accelerated deterioration of spatial learning/memory. Notably, introduction of a signal transduction-defective mutant RAGE (DN-RAGE) to microglia attenuates deterioration induced by Abeta. These findings indicate that RAGE signaling in microglia contributes to the pathogenesis of an inflammatory response that ultimately impairs neuronal function and directly affects amyloid accumulation. We conclude that blockade of microglial RAGE may have a beneficial effect on Abeta-mediated neuronal perturbation relevant to AD pathogenesis.-Fang, F., Lue, L.-F., Yan, S., Xu, H., Luddy, J. S., Chen, D., Walker, D. G., Stern, D. M., Yan, S., Schmidt, A. M., Chen, J. X., Yan, S. S. RAGE-dependent signaling in microglia contributes to neuroinflammation, Abeta accumulation, and impaired learning/memory in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.
Figures

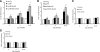
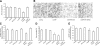
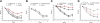
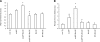
References
-
- Uchihara T., Akiyama H., Kondo H., Ikeda K. Activated microglial cells are colocalized with perivascular deposits of amyloid-beta protein in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Stroke. 1997;28:1948–1950. - PubMed
-
- Giulian D., Li J., Leara B., Keenen C. Phagocytic microglia release cytokines and cytotoxins that regulate the survival of astrocytes and neurons in culture. Neurochem Int. 1994;25:227–233. - PubMed
-
- McGeer P. L., Rogers J., McGeer E. G. Inflammation, anti-inflammatory agents and Alzheimer disease: the last 12 years. J Alzheimers Dis. 2006;9:271–276. - PubMed
-
- Giulian D., Haverkamp L. J., Li J., Karshin W. L., Yu J., Tom D., Li X., Kirkpatrick J. B. Senile plaques stimulate microglia to release a neurotoxin found in Alzheimer brain. Neurochem Int. 1995;27:119–137. - PubMed
-
- Minghetti L. Role of inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Opin Neurol. 2005;18:315–321. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

