PRGdb: a bioinformatics platform for plant resistance gene analysis
- PMID: 19906694
- PMCID: PMC2808903
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp978
PRGdb: a bioinformatics platform for plant resistance gene analysis
Abstract
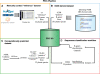
PRGdb is a web accessible open-source (http://www.prgdb.org) database that represents the first bioinformatic resource providing a comprehensive overview of resistance genes (R-genes) in plants. PRGdb holds more than 16,000 known and putative R-genes belonging to 192 plant species challenged by 115 different pathogens and linked with useful biological information. The complete database includes a set of 73 manually curated reference R-genes, 6308 putative R-genes collected from NCBI and 10463 computationally predicted putative R-genes. Thanks to a user-friendly interface, data can be examined using different query tools. A home-made prediction pipeline called Disease Resistance Analysis and Gene Orthology (DRAGO), based on reference R-gene sequence data, was developed to search for plant resistance genes in public datasets such as Unigene and Genbank. New putative R-gene classes containing unknown domain combinations were discovered and characterized. The development of the PRG platform represents an important starting point to conduct various experimental tasks. The inferred cross-link between genomic and phenotypic information allows access to a large body of information to find answers to several biological questions. The database structure also permits easy integration with other data types and opens up prospects for future implementations.
Figures


References
-
- Flor HH. Current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Annual Rev. Phytopathol. 1971;9:275–296.
-
- Ellis J, Dodds P, Pryor T. The generation of plant disease resistance gene specificities. Trends Plant Sci. 2000;5:373–379. - PubMed
-
- Chisholm ST, Coaker G, Day B, Staskawicz BJ. Host-microbe interactions: shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell. 2006;124:803–814. - PubMed
-
- Means TK, Golenbock DT, Fenton MJ. The biology of Toll-like receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2000;11:219–232. - PubMed
-
- Mackey D, Holt BF, Wiig A, Dangl JL. RIN4 interacts with Pseudomonas syringae type III effector molecules and is required for RPM1-mediated resistance in Arabidopsis. Cell. 2002;108:743–754. - PubMed

