Cohesin promotes the repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in replicated chromatin
- PMID: 19906707
- PMCID: PMC2811025
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkp976
Cohesin promotes the repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in replicated chromatin
Abstract
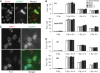
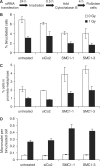
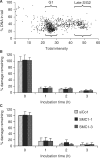
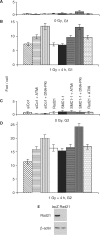
The cohesin protein complex holds sister chromatids together after synthesis until mitosis. It also contributes to post-replicative DNA repair in yeast and higher eukaryotes and accumulates at sites of laser-induced damage in human cells. Our goal was to determine whether the cohesin subunits SMC1 and Rad21 contribute to DNA double-strand break repair in X-irradiated human cells in the G2 phase of the cell cycle. RNA interference-mediated depletion of SMC1 sensitized HeLa cells to X-rays. Repair of radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks, measured by gammaH2AX/53BP1 foci analysis, was slower in SMC1- or Rad21-depleted cells than in controls in G2 but not in G1. Inhibition of the DNA damage kinase DNA-PK, but not ATM, further inhibited foci loss in cohesin-depleted cells in G2. SMC1 depletion had no effect on DNA single-strand break repair in either G1 or late S/G2. Rad21 and SMC1 were recruited to sites of X-ray-induced DNA damage in G2-phase cells, but not in G1, and only when DNA damage was concentrated in subnuclear stripes, generated by partially shielded ultrasoft X-rays. Our results suggest that the cohesin complex contributes to cell survival by promoting the repair of radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in G2-phase cells in an ATM-dependent pathway.
Figures

References
-
- Jackson SP. Sensing and repairing DNA double-strand breaks. Carcinogenesis. 2002;23:687–696. - PubMed
-
- Rothkamm K. Different means to an end: DNA double-strand break repair. In: Kiefer J, editor. Life Science and Radiation: Accomplishments and Future Directions. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer; 2004. pp. 179–186.
-
- Hinz JM, Yamada NA, Salazar EP, Tebbs RS, Thompson LH. Influence of double-strand-break repair pathways on radiosensitivity throughout the cell cycle in CHO cells. DNA Repair. 2005;4:782–792. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

