Bayesian inference of species trees from multilocus data
- PMID: 19906793
- PMCID: PMC2822290
- DOI: 10.1093/molbev/msp274
Bayesian inference of species trees from multilocus data
Abstract
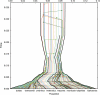
Until recently, it has been common practice for a phylogenetic analysis to use a single gene sequence from a single individual organism as a proxy for an entire species. With technological advances, it is now becoming more common to collect data sets containing multiple gene loci and multiple individuals per species. These data sets often reveal the need to directly model intraspecies polymorphism and incomplete lineage sorting in phylogenetic estimation procedures. For a single species, coalescent theory is widely used in contemporary population genetics to model intraspecific gene trees. Here, we present a Bayesian Markov chain Monte Carlo method for the multispecies coalescent. Our method coestimates multiple gene trees embedded in a shared species tree along with the effective population size of both extant and ancestral species. The inference is made possible by multilocus data from multiple individuals per species. Using a multiindividual data set and a series of simulations of rapid species radiations, we demonstrate the efficacy of our new method. These simulations give some insight into the behavior of the method as a function of sampled individuals, sampled loci, and sequence length. Finally, we compare our new method to both an existing method (BEST 2.2) with similar goals and the supermatrix (concatenation) method. We demonstrate that both BEST and our method have much better estimation accuracy for species tree topology than concatenation, and our method outperforms BEST in divergence time and population size estimation.
Figures
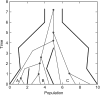
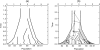
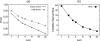

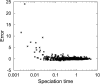
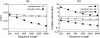
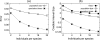

References
-
- Belfiore NM, Liu L, Moritz C. Multilocus phylogenetics of a rapid radiation in the genus Thomomys (Rodentia: Geomyidae) Syst Biol. 2008;57(2):294. - PubMed
-
- Degnan JH, Rosenberg NA. Gene tree discordance, phylogenetic inference and the multispecies coalescent. Trends Ecol Evol. 2009;24(6):332–340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

