Higher selenium status is associated with adverse blood lipid profile in British adults
- PMID: 19906812
- PMCID: PMC2793123
- DOI: 10.3945/jn.109.111252
Higher selenium status is associated with adverse blood lipid profile in British adults
Abstract
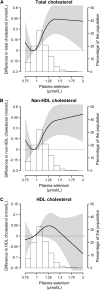
Recent findings have raised concern about possible associations of high selenium exposure with diabetes and hyperlipidemia in the US, a population with high selenium status. In the UK, a population with lower selenium status, there is little data on the association of selenium status with cardio-metabolic risk factors in the general population. We examined the association of plasma selenium concentration with blood lipids in a nationally representative sample of British adults. A cross-sectional study was conducted among 1042 white participants (aged 19-64 y) in the 2000-2001 UK National Diet and Nutrition Survey. Plasma selenium was measured by inductively coupled-plasma mass spectrometry. Total and HDL cholesterol were measured in nonfasting plasma samples. Mean plasma selenium concentration was 1.10 +/- 0.19 micromol/L. The multivariate adjusted differences between the highest (> or =1.20 micromol/L) and lowest (<0.98 micromol/L) quartiles of plasma selenium were 0.39 (95% CI 0.18, 0.60) mmol/L for total cholesterol, 0.38 (0.17, 0.59) for non-HDL cholesterol, and 0.01 (-0.05, 0.07) for HDL cholesterol. Higher plasma selenium (i.e., > or =1.20 micromol/L) was associated with increased total and non-HDL cholesterol levels but not with HDL in the UK adult population. These findings raise additional concern about potential adverse cardio-metabolic effects of high selenium status. Randomized and mechanistic evidence is necessary to assess causality and to evaluate the impact of this association on cardiovascular risk.
Figures
References
-
- Navas-Acien A, Bleys J, Guallar E. Selenium intake and cardiovascular risk - what is new? Curr Opin Lipidol. 2008;19:43–9. - PubMed
-
- Rayman MP. Food-chain selenium and human health: emphasis on intake. Br J Nutr. 2008;100:254–68. - PubMed
-
- Burk RF. Selenium, an antioxidant nutrient. Nutr Clin Care. 2002;5:75–9. - PubMed
-
- Papp LV, Lu J, Holmgren A, Khanna KK. From selenium to selenoproteins: synthesis, identity, and their role in human health. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2007;9:775–806. - PubMed
-
- Bleys J, Navas-Acien A, Guallar E. Serum selenium and diabetes in U.S. Adults. Diabetes Care. 2007;30:829–34. - PubMed

