The challenges of informatics in synthetic biology: from biomolecular networks to artificial organisms
- PMID: 19906839
- PMCID: PMC2810114
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbp054
The challenges of informatics in synthetic biology: from biomolecular networks to artificial organisms
Abstract
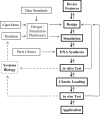
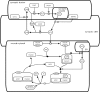
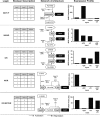
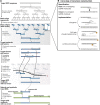
The field of synthetic biology holds an inspiring vision for the future; it integrates computational analysis, biological data and the systems engineering paradigm in the design of new biological machines and systems. These biological machines are built from basic biomolecular components analogous to electrical devices, and the information flow among these components requires the augmentation of biological insight with the power of a formal approach to information management. Here we review the informatics challenges in synthetic biology along three dimensions: in silico, in vitro and in vivo. First, we describe state of the art of the in silico support of synthetic biology, from the specific data exchange formats, to the most popular software platforms and algorithms. Next, we cast in vitro synthetic biology in terms of information flow, and discuss genetic fidelity in DNA manipulation, development strategies of biological parts and the regulation of biomolecular networks. Finally, we explore how the engineering chassis can manipulate biological circuitries in vivo to give rise to future artificial organisms.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Macromolecular crowding: chemistry and physics meet biology (Ascona, Switzerland, 10-14 June 2012).Phys Biol. 2013 Aug;10(4):040301. doi: 10.1088/1478-3975/10/4/040301. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Phys Biol. 2013. PMID: 23912807
-
Xenobiology: State-of-the-Art, Ethics, and Philosophy of New-to-Nature Organisms.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2018;162:301-315. doi: 10.1007/10_2016_14. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 28567486 Review.
-
Tunable promoters in synthetic and systems biology.Subcell Biochem. 2012;64:181-201. doi: 10.1007/978-94-007-5055-5_9. Subcell Biochem. 2012. PMID: 23080251 Review.
-
[Machine learning-aided design of synthetic biological parts and circuits].Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2025 Mar 25;41(3):1023-1051. doi: 10.13345/j.cjb.240605. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2025. PMID: 40170311 Review. Chinese.
-
In silico implementation of synthetic gene networks.Methods Mol Biol. 2012;813:3-21. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-412-4_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22083733 Review.
Cited by
-
Boosting forward-time population genetic simulators through genotype compression.BMC Bioinformatics. 2013 Jun 14;14:192. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-14-192. BMC Bioinformatics. 2013. PMID: 23763838 Free PMC article.
-
Confidence from uncertainty--a multi-target drug screening method from robust control theory.BMC Syst Biol. 2010 Nov 24;4:161. doi: 10.1186/1752-0509-4-161. BMC Syst Biol. 2010. PMID: 21106087 Free PMC article.
-
Translational cross talk in gene networks.Biophys J. 2013 Jun 4;104(11):2564-72. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.04.049. Biophys J. 2013. PMID: 23746529 Free PMC article.
-
Rise and demise of bioinformatics? Promise and progress.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(4):e1002487. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002487. Epub 2012 Apr 26. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 22570600 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-platform microarray data normalisation for regulatory network inference.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 12;5(11):e13822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013822. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21103045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barrett CL, Kim TY, Kim HU, et al. Systems biology as a foundation for genome-scale synthetic biology. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2006;17:488–92. - PubMed
-
- Lee SK, Chou H, Ham TS, et al. Metabolic engineering of microorganisms for biofuels production: from bugs to synthetic biology to fuels. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2008;19:556–63. - PubMed
-
- Chang MCY, Keasling JD. Production of isoprenoid pharmaceuticals by engineered microbes. Nat Chem Biol. 2006;2:674–81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

