Drosophila laminins act as key regulators of basement membrane assembly and morphogenesis
- PMID: 19906841
- PMCID: PMC2781052
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.044263
Drosophila laminins act as key regulators of basement membrane assembly and morphogenesis
Abstract
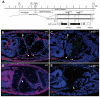
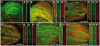
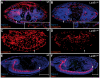
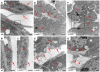
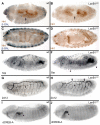
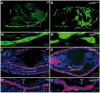
Laminins are heterotrimeric molecules found in all basement membranes. In mammals, they have been involved in diverse developmental processes, from gastrulation to tissue maintenance. The Drosophila genome encodes two laminin alpha chains, one beta and one Gamma, which form two distinct laminin trimers. So far, only mutations affecting one or other trimer have been analysed. In order to study embryonic development in the complete absence of laminins, we mutated the gene encoding the sole laminin beta chain in Drosophila, LanB1, so that no trimers can be made. We show that LanB1 mutant embryos develop until the end of embryogenesis. Electron microscopy analysis of mutant embryos reveals that the basement membranes are absent and the remaining extracellular material appears disorganised and diffuse. Accordingly, abnormal accumulation of major basement membrane components, such as Collagen IV and Perlecan, is observed in mutant tissues. In addition, we show that elimination of LanB1 prevents the normal morphogenesis of most organs and tissues, including the gut, trachea, muscles and nervous system. In spite of the above structural roles for laminins, our results unravel novel functions in cell adhesion, migration and rearrangement. We propose that while an early function of laminins in gastrulation is not conserved in Drosophila and mammals, their function in basement membrane assembly and organogenesis seems to be maintained throughout evolution.
Figures



References
-
- Andrew D. J., Baig A., Bhanot P., Smolik S. M., Henderson K. D. (1997). The Drosophila dCREB-A gene is required for dorsal/ventral patterning of the larval cuticle. Development 124, 181-193 - PubMed
-
- Aumailley M., Bruckner-Tuderman L., Carter W. G., Deutzmann R., Edgar D., Yamada Y., Yurchenco P. D. (2005). A simplified laminin nomenclature. Matrix Biol. 24, 326-332 - PubMed
-
- Bate M. (1990). The embryonic development of larval muscles in Drosophila. Development 110, 791-804 - PubMed
-
- Benson S., Page L., Ingersoll E., Rosenthal E., Dungca K., Signor D. (1999). Developmental characterization of the gene for laminin alpha-chain in sea urchin embryos. Mech. Dev. 81, 37-49 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

