Coordination of sonic hedgehog and Wnt signaling determines ventral and dorsal telencephalic neuron types from human embryonic stem cells
- PMID: 19906872
- PMCID: PMC2778748
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.036624
Coordination of sonic hedgehog and Wnt signaling determines ventral and dorsal telencephalic neuron types from human embryonic stem cells
Abstract
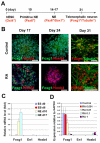
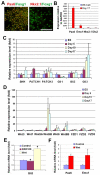
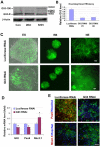
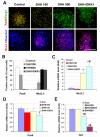
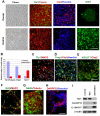
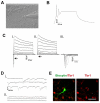
The directed differentiation of forebrain neuronal types from human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) has not been achieved. Here, we show that hESCs differentiate to telencephalic progenitors with a predominantly dorsal identity in a chemically defined medium without known morphogens. This is attributed to endogenous Wnt signaling, which upregulates the truncated form of GLI3, a repressor of sonic hedgehog (SHH). A high concentration of SHH, or the inhibition of Wnt by dickkopf 1 (DKK1) together with a low concentration of SHH, almost completely converts the primitive dorsal precursors to ventral progenitors, which is partially achieved through both downregulation of the truncated GLI3 and upregulation of full-length GLI3 expression. These dorsal and ventral telencephalic progenitors differentiate to functional glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons, respectively. Thus, although hESCs generate dorsal telencephalic cells, as opposed to ventral progenitors in other vertebrates, in the absence of exogenous morphogens, human cells use a similar molecular mechanism to control the dorsal versus ventral fate. The coordination of Wnt and SHH signaling through GLI3 represents a novel mechanism that regulates ventral-dorsal patterning in the development of forebrain neuronal subtypes.
Figures
References
-
- Ahn S., Joyner A. L. (2004). Dynamic changes in the response of cells to positive hedgehog signaling during mouse limb patterning. Cell 118, 505-516 - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Medina R., Cayuso J., Okubo T., Takada S., Marti E. (2008). Wnt canonical pathway restricts graded Shh/Gli patterning activity through the regulation of Gli3 expression. Development 135, 237-247 - PubMed
-
- Anderson K. D., Reiner A. (1991). Immunohistochemical localization of DARPP-32 in striatal projection neurons and striatal interneurons: implications for the localization of D1-like dopamine receptors on different types of striatal neurons. Brain Res. 568, 235-243 - PubMed
-
- Arlotta P., Molyneaux B. J., Chen J., Inoue J., Kominami R., Macklis J. D. (2005). Neuronal subtype-specific genes that control corticospinal motor neuron development in vivo. Neuron 45, 207-221 - PubMed
-
- Bai C. B., Stephen D., Joyner A. L. (2004). All mouse ventral spinal cord patterning by hedgehog is Gli dependent and involves an activator function of Gli3. Dev. Cell 6, 103-115 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

