Involvement of reactive oxygen species in long-term potentiation in the spinal cord dorsal horn
- PMID: 19906875
- PMCID: PMC2807226
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.90906.2008
Involvement of reactive oxygen species in long-term potentiation in the spinal cord dorsal horn
Abstract
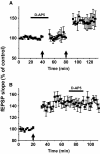
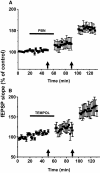
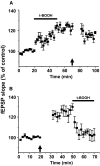
Recent studies suggest that reactive oxygen species (ROS) are functional messenger molecules in central sensitization, an underlying mechanism of persistent pain. Because spinal cord long-term potentiation (LTP) is the electrophysiological basis of central sensitization, this study investigates the effects of the increased or decreased spinal ROS levels on spinal cord LTP. Spinal cord LTP is induced by either brief, high-frequency stimulation (HFS) of a dorsal root at C-fiber intensity or superfusion of a ROS donor, tert-butyl hydroperoxide (t-BOOH), onto rat spinal cord slice preparations. Field excitatory postsynaptic potentials (fEPSPs) evoked by dorsal root stimulations with either Abeta- or C-fiber intensity are recorded from the superficial dorsal horn. HFS significantly increases the slope of both Abeta- and C-fiber evoked fEPSPs, thus suggesting LTP development. The induction, not the maintenance, of HFS-induced LTP is blocked by a N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor antagonist, D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (D-AP5). Both the induction and maintenance of LTP of Abeta-fiber-evoked fEPSPs are inhibited by a ROS scavenger, either N-tert-butyl-alpha-phenylnitrone or 4-hydroxy-2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-N-oxyl. A ROS donor, t-BOOH-induced LTP is inhibited by N-tert-butyl-alpha-phenylnitrone but not by D-AP5. Furthermore, HFS-induced LTP and t-BOOH-induced LTP occlude each other. The data suggest that elevated ROS is a downstream event of NMDA receptor activation and an essential step for potentiation of synaptic excitability in the spinal dorsal horn.
Figures
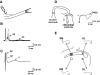
 , 6–8 of 10 samples; ○, 1–3 of 10 samples; ×, 0 of 10 samples). Typical examples of raw traces of fEPSP from each location (SM, SL, DM, and DL) are shown. Calibration bars are 3 ms and 0.1 mV. Note that most of fEPSPs (6 of 10) from DM have multiple peaks.
, 6–8 of 10 samples; ○, 1–3 of 10 samples; ×, 0 of 10 samples). Typical examples of raw traces of fEPSP from each location (SM, SL, DM, and DL) are shown. Calibration bars are 3 ms and 0.1 mV. Note that most of fEPSPs (6 of 10) from DM have multiple peaks.


Similar articles
-
Reactive oxygen species enhance excitatory synaptic transmission in rat spinal dorsal horn neurons by activating TRPA1 and TRPV1 channels.Neuroscience. 2013 Sep 5;247:201-12. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.05.023. Epub 2013 May 22. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 23707800
-
[Role of phospho-calcium/ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in the induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation of C-fiber-evoked field potentials in spinal dorsal horn of the rat].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2004 Feb 25;56(1):83-8. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2004. PMID: 14985835 Chinese.
-
Ryanodine receptors contribute to the induction of nociceptive input-evoked long-term potentiation in the rat spinal cord slice.Mol Pain. 2010 Jan 20;6:1. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-6-1. Mol Pain. 2010. PMID: 20089138 Free PMC article.
-
Dorsal horn alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor trafficking in inflammatory pain.Anesthesiology. 2010 May;112(5):1259-65. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181d3e1ed. Anesthesiology. 2010. PMID: 20395828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-term potentiation in spinal nociceptive pathways as a novel target for pain therapy.Mol Pain. 2011 Mar 28;7:20. doi: 10.1186/1744-8069-7-20. Mol Pain. 2011. PMID: 21443797 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prooxidant-induced c-Src/nuclear factor kappa B-coupled signalling in sensory ganglia mediates cutaneous hyperalgesia.Eur J Pain. 2013 Aug;17(7):1027-38. doi: 10.1002/j.1532-2149.2012.00273.x. Epub 2012 Dec 27. Eur J Pain. 2013. PMID: 23280824 Free PMC article.
-
Early oxidative stress and DNA damage in Aβ-burdened hippocampal neurons in an Alzheimer's-like transgenic rat model.Commun Biol. 2024 Jul 14;7(1):861. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06552-4. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39004677 Free PMC article.
-
Antinociceptive drug interaction between intrathecal vitamin E and gabapentin in the rat formalin test.Korean J Anesthesiol. 2012 Nov;63(5):447-53. doi: 10.4097/kjae.2012.63.5.447. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2012. PMID: 23198040 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial hydrogen peroxide positively regulates neuropeptide secretion during diet-induced activation of the oxidative stress response.Nat Commun. 2021 Apr 16;12(1):2304. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-22561-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33863916 Free PMC article.
-
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate Oxidases Are Everywhere in Brain Disease, but Not in Huntington's Disease?Front Aging Neurosci. 2021 Nov 5;13:736734. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.736734. eCollection 2021. Front Aging Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34803655 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arancio O, Kiebler M, Lee CJ, Lev-Ram V, Tsien RY, Kandel ER, Hawkins RD. Nitric oxide acts directly in the presynaptic neuron to produce long-term potentiation in cultured hippocampal neurons. Cell 87: 1025–1035, 1996 - PubMed
-
- Bennett GJ, Abdelmoumene M, Hayashi H, Dubner R. Physiology and morphology of substantia gelatinosa neurons intracellularly stained with horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol 194: 809–827, 1980 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

