Specific roles of AMPA receptor subunit GluR1 (GluA1) phosphorylation sites in regulating synaptic plasticity in the CA1 region of hippocampus
- PMID: 19906877
- PMCID: PMC2807233
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00835.2009
Specific roles of AMPA receptor subunit GluR1 (GluA1) phosphorylation sites in regulating synaptic plasticity in the CA1 region of hippocampus
Abstract
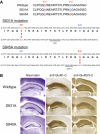
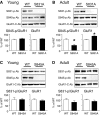
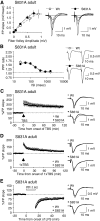
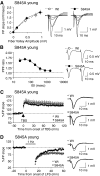
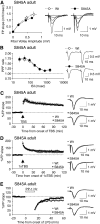
Activity-dependent changes in excitatory synaptic transmission in the CNS have been shown to depend on the regulation of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptors (AMPARs). In particular, several lines of evidence suggest that reversible phosphorylation of AMPAR subunit glutamate receptor 1 (GluR1, also referred to as GluA1 or GluR-A) plays a role in long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD). We previously reported that regulation of serines (S) 831 and 845 on the GluR1 subunit may play a critical role in bidirectional synaptic plasticity in the Schaffer collateral inputs to CA1. Specifically, gene knockin mice lacking both S831 and S845 phosphorylation sites ("double phosphomutants"), where both serine residues were replaced by alanines (A), showed a faster decaying LTP and a deficit in LTD. To determine which of the two phosphorylation sites was responsible for the phenotype, we have now generated two lines of gene knockin mice: one that specifically lacks S831 (S831A mutants) and another that lacks only S845 (S845A mutants). We found that S831A mutants display normal LTP and LTD, whereas S845A mutants show a specific deficit in LTD. Taken together with our previous results from the "double phosphomutants," our data suggest that either S831 or S845 alone may support LTP, whereas the S845 site is critical for LTD expression.
Figures

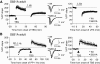
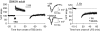
References
-
- Barria A, Derkach V, Soderling T. Identification of the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II regulatory phosphorylation site in the α-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate type gluatamate receptor. J Biol Chem 272: 32727–32730, 1997a - PubMed
-
- Barria A, Muller D, Derkach V, Griffith LC, Soderling TR. Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaM-KII during long-term potentiation. Science 276: 2042–2045, 1997b - PubMed
-
- Benke TA, Luthi A, Isaac JT, Collingridge GL. Modulation of AMPA receptor unitary conductance by synaptic activity. Nature 393: 793–797, 1998 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

