Wide-scale use of Notch signaling factor CSL/RBP-Jkappa in RTA-mediated activation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic genes
- PMID: 19906914
- PMCID: PMC2812342
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01301-09
Wide-scale use of Notch signaling factor CSL/RBP-Jkappa in RTA-mediated activation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus lytic genes
Abstract
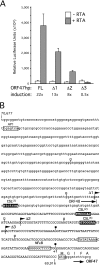
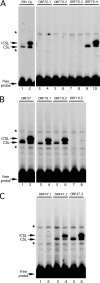
For Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV; also called human herpesvirus 8 [HHV8]), the switch from latency to active lytic replication requires RTA, the product of open reading frame 50 (ORF50). RTA activates transcription from nearly 40 early and delayed-early viral promoters, mainly through interactions with cellular DNA binding proteins, such as CSL/RBP-Jkappa, Oct-1, C/EBPalpha, and c-Jun. Reliance on cellular coregulators may allow KSHV to adjust its lytic program to suit different cellular contexts or interpret signals from the outside. CSL is a key component of the Notch signaling pathway and is targeted by several viruses. A search with known CSL binding sequences from cellular genes found at least 260 matches in the KSHV genome, many from regions containing known or suspected lytic promoters. Analysis of clustered sites located immediately upstream of ORF70 (thymidylate synthase), ORF19 (tegument protein), and ORF47 (glycoprotein L) uncovered RTA-responsive promoters that were validated using mRNAs isolated from KSHV-infected cells undergoing lytic reactivation. Notably, ORF19 behaves as a true late gene, indicating that RTA regulates all three phases of the lytic program. For each new promoter, the response to RTA was dependent on CSL, and 5 of the 10 candidate sites were shown to bind CSL in vitro. Analysis of individual sites highlighted the importance of a cytosine residue flanking the core CSL binding sequence. These findings broaden the role for CSL in coordinating the KSHV lytic gene expression program and help to define a signature motif for functional CSL sites within the viral genome.
Figures







References
-
- Bray, S. J. 2006. Notch signalling: a simple pathway becomes complex. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7:678-689. - PubMed
-
- Carroll, K. D., F. Khadim, S. Spadavecchia, D. Palmeri, and D. M. Lukac. 2007. Direct interactions of KSHV/HHV-8 ORF50/Rta protein with the cellular protein octamer-1 and DNA are critical for specifying transactivation of a delayed-early promoter and stimulating viral reactivation. J. Virol. 81:8451-8467. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang, J., and D. Ganem. 2000. On the control of late gene expression in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus-8). J. Gen. Virol. 81:2039-2047. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

