Trafficking of membrane proteins to cone but not rod outer segments is dependent on heterotrimeric kinesin-II
- PMID: 19906976
- PMCID: PMC2788486
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3976-09.2009
Trafficking of membrane proteins to cone but not rod outer segments is dependent on heterotrimeric kinesin-II
Abstract
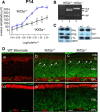
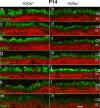
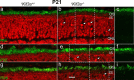
Heterotrimeric kinesin-II is a molecular motor localized to the inner segment, connecting cilium and axoneme of mammalian photoreceptors. Our purpose was to identify the role of kinesin-II in anterograde intraflagellar transport by photoreceptor-specific deletions of kinesin family member 3A (KIF3A), its obligatory motor subunit. In cones lacking KIF3A, membrane proteins involved in phototransduction did not traffic to the outer segments resulting in complete absence of a photopic electroretinogram and progressive cone degeneration. Rod photoreceptors lacking KIF3A degenerated rapidly between 2 and 4 weeks postnatally, but the phototransduction components including rhodopsin trafficked to the outer segments during the course of degeneration. Furthermore, KIF3A deletion did not affect synaptic anterograde trafficking. The results indicate that trafficking of membrane proteins to the outer segment is dependent on kinesin-II in cone, but not rod photoreceptors, even though rods and cones share similar structures, and closely related phototransduction polypeptides.
Figures


References
-
- Anderson DH, Fisher SK, Steinberg RH. Mammalian cones: disc shedding, phagocytosis, and renewal. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1978;17:117–133. - PubMed
-
- Applebury ML, Antoch MP, Baxter LC, Chun LL, Falk JD, Farhangfar F, Kage K, Krzystolik MG, Lyass LA, Robbins JT. The murine cone photoreceptor: a single cone type expresses both S and M opsins with retinal spatial patterning. Neuron. 2000;27:513–523. - PubMed
-
- Baker SA, Freeman K, Luby-Phelps K, Pazour GJ, Besharse JC. IFT20 links kinesin II with a mammalian intraflagellar transport complex that is conserved in motile flagella and sensory cilia. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:34211–34218. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 EY019298/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY013811/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 EY013811/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY007042/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY014800-039003/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY13408/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY019298/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY008123/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013408/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EY013811/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY08123/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 EY014800/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- EY07042/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
