Limiting dilution analysis of murine epidermal stem cells using an in vivo regeneration assay
- PMID: 19908020
- PMCID: PMC2783164
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-60761-380-0_29
Limiting dilution analysis of murine epidermal stem cells using an in vivo regeneration assay
Abstract
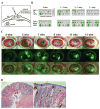
Epidermal stem cells are of major importance for tissue homeostasis, wound repair, tumor initiation, and gene therapy. Here we describe an in vivo regeneration assay to test for the ability of keratinocyte progenitors to maintain an epidermis over the long-term in vivo. Limiting dilution analysis of epidermal repopulating units in this in vivo regeneration assay at sequential time points allows the frequency of short-term (transit amplifying cell) and long-term (stem cell) repopulating cells to be quantified.
Figures
References
-
- Hodgson GS, Bradley TR. Properties of haematopoietic stem cells surviving 5-fluorouracil treatment: evidence for a pre-CFU-S cell? Nature. 1979;281(5730):381–2. - PubMed
-
- Lerner C, Harrison DE. 5-Fluorouracil spares hemopoietic stem cells responsible for long-term repopulation. Exp Hematol. 1990;18(2):114–8. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

