Progression to microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes: development and validation of a prediction rule
- PMID: 19908023
- PMCID: PMC2797626
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-009-1585-3
Progression to microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes: development and validation of a prediction rule
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: Microalbuminuria is common in type 1 diabetes and is associated with an increased risk of renal and cardiovascular disease. We aimed to develop and validate a clinical prediction rule that estimates the absolute risk of microalbuminuria.
Methods: Data from the European Diabetes Prospective Complications Study (n = 1115) were used to develop the prediction rule (development set). Multivariable logistic regression analysis was used to assess the association between potential predictors and progression to microalbuminuria within 7 years. The performance of the prediction rule was assessed with calibration and discrimination (concordance statistic [c-statistic]) measures. The rule was validated in three other diabetes studies (Pittsburgh Epidemiology of Diabetes Complications [EDC] study, Finnish Diabetic Nephropathy [FinnDiane] study and Coronary Artery Calcification in Type 1 Diabetes [CACTI] study).
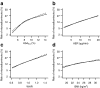
Results: Of patients in the development set, 13% were microalbuminuric after 7 years. Glycosylated haemoglobin, AER, WHR, BMI and ever smoking were found to be the most important predictors. A high-risk group (n = 87 [8%]) was identified with a risk of progression to microalbuminuria of 32%. Predictions showed reasonable discriminative ability, with c-statistic of 0.71. The rule showed good calibration and discrimination in EDC, FinnDiane and CACTI (c-statistic 0.71, 0.79 and 0.79, respectively).
Conclusions/interpretation: We developed and validated a clinical prediction rule that uses relatively easily obtainable patient characteristics to predict microalbuminuria in patients with type 1 diabetes. This rule can help clinicians to decide on more frequent check-ups for patients at high risk of microalbuminuria in order to prevent long-term chronic complications.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

