A proposed algorithm for initiation of renal replacement therapy in adult critically ill patients
- PMID: 19909493
- PMCID: PMC2811906
- DOI: 10.1186/cc8037
A proposed algorithm for initiation of renal replacement therapy in adult critically ill patients
Abstract
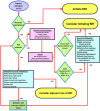
Critically ill patients whose course is complicated by acute kidney injury often receive renal replacement therapy (RRT). For these patients, initiation of RRT results in a considerable escalation in both the complexity and associated cost of care. While RRT is extensively used in clinical practice, there remains uncertainty about the ideal circumstances of when to initiate RRT and for what indications. The process of deciding when to initiate RRT in critically ill patients is complex and is influenced by numerous factors, including patient-specific and clinician-specific factors and those related to local organizational/logistical issues. Studies have shown marked variation between clinicians, and across institutions and countries. As a consequence, analysis of ideal circumstances under which to initiate RRT is challenging. Recognizing this limitation, we review the available data and propose a clinical algorithm to aid in the decision for RRT initiation in critically ill adult patients. The algorithm incorporates several patient-specific factors, based on evidence when available, that may decisively influence when to initiate RRT. The objective of this algorithm is to provide a starting point to guide clinicians on when to initiate RRT in critically ill adult patients. In addition, the proposed algorithm is intended to provide a foundation for prospective evaluation and the development of a broad consensus on when to initiate RRT in critically ill patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Renal replacement therapy: when to start.Contrib Nephrol. 2011;174:232-241. doi: 10.1159/000329401. Epub 2011 Sep 9. Contrib Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21921628 Review.
-
Renal replacement therapy in adult critically ill patients: when to begin and when to stop.Contrib Nephrol. 2010;165:263-273. doi: 10.1159/000313766. Epub 2010 Apr 20. Contrib Nephrol. 2010. PMID: 20427977
-
Renal replacement therapy in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury--when to start.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012 Jun;27(6):2242-8. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr707. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012. PMID: 22231034
-
When should renal replacement therapy for acute kidney injury be initiated and discontinued?Blood Purif. 2008;26(5):473-84. doi: 10.1159/000157325. Epub 2008 Sep 22. Blood Purif. 2008. PMID: 18810230 Review.
-
Timing of renal replacement therapy initiation for acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: a systematic review of randomized clinical trials with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.Crit Care. 2021 Jan 6;25(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03451-y. Crit Care. 2021. PMID: 33407756 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Classification and staging of acute kidney injury: beyond the RIFLE and AKIN criteria.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011 Apr;7(4):201-8. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2011.14. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21364520 Review.
-
Treatment of Acute Kidney Injury: A Review of Current Approaches and Emerging Innovations.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 23;13(9):2455. doi: 10.3390/jcm13092455. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38730983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors associated with poor outcomes of continuous renal replacement therapy.PLoS One. 2017 May 24;12(5):e0177759. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0177759. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28542272 Free PMC article.
-
Transitions and Long-Term Clinical Outcomes in Patients Admitted in Intensive Care Units Receiving Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 27;13(17):5085. doi: 10.3390/jcm13175085. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39274298 Free PMC article.
-
Timing of kidney replacement therapy in critically ill patients: A call to shift the paradigm in the era of artificial intelligence.Sci Prog. 2025 Apr-Jun;108(2):368504251338927. doi: 10.1177/00368504251338927. Epub 2025 Apr 24. Sci Prog. 2025. PMID: 40275676 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bagshaw SM, Laupland KB, Doig CJ, Mortis G, Fick GH, Mucenski M, Godinez-Luna T, Svenson LW, Rosenal T. Prognosis for long-term survival and renal recovery in critically ill patients with severe acute renal failure: a population-based study. Crit Care. 2005;9:R700–R709. doi: 10.1186/cc3879. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, Schetz M, Tan I, Bouman C, Macedo E, Gibney N, Tolwani A, Ronco C. Beginning and Ending Supportive Therapy for the Kidney (BEST Kidney) Investigators. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;294:813–818. doi: 10.1001/jama.294.7.813. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cruz DN, Bolgan I, Perazella MA, Bonello M, de Cal M, Corradi V, Polanco N, Ocampo C, Nalesso F, Piccinni P, Ronco C. North East Italian Prospective Hospital Renal Outcome Survey on Acute Kidney Injury (NEiPHROS-AKI): targeting the problem with the RIFLE Criteria. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;2:418–425. doi: 10.2215/CJN.03361006. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

